Drip irrigation system
Drip irrigation system
About Drip Irrigation System
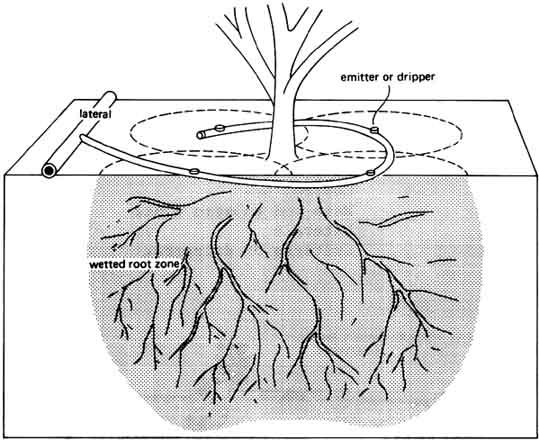
Drip irrigation system delivers water to the crop using a network of mainlines, sub-mains and lateral lines with emission points spaced along their lengths.
Each dripper/emitter, orifice supplies a measured, precisely controlled uniform application of water, nutrients, and other required growth substances directly into the root zone of the plant.
Water and nutrients enter the soil from the emitters, moving into the root zone of the plants through the combined forces of gravity and capillary. In this way, the plant’s withdrawal of moisture and nutrients are replenished almost immediately, ensuring that the plant never suffers from water stress, thus enhancing quality, its ability to achieve optimum growth and high yield.
Drip System Layout
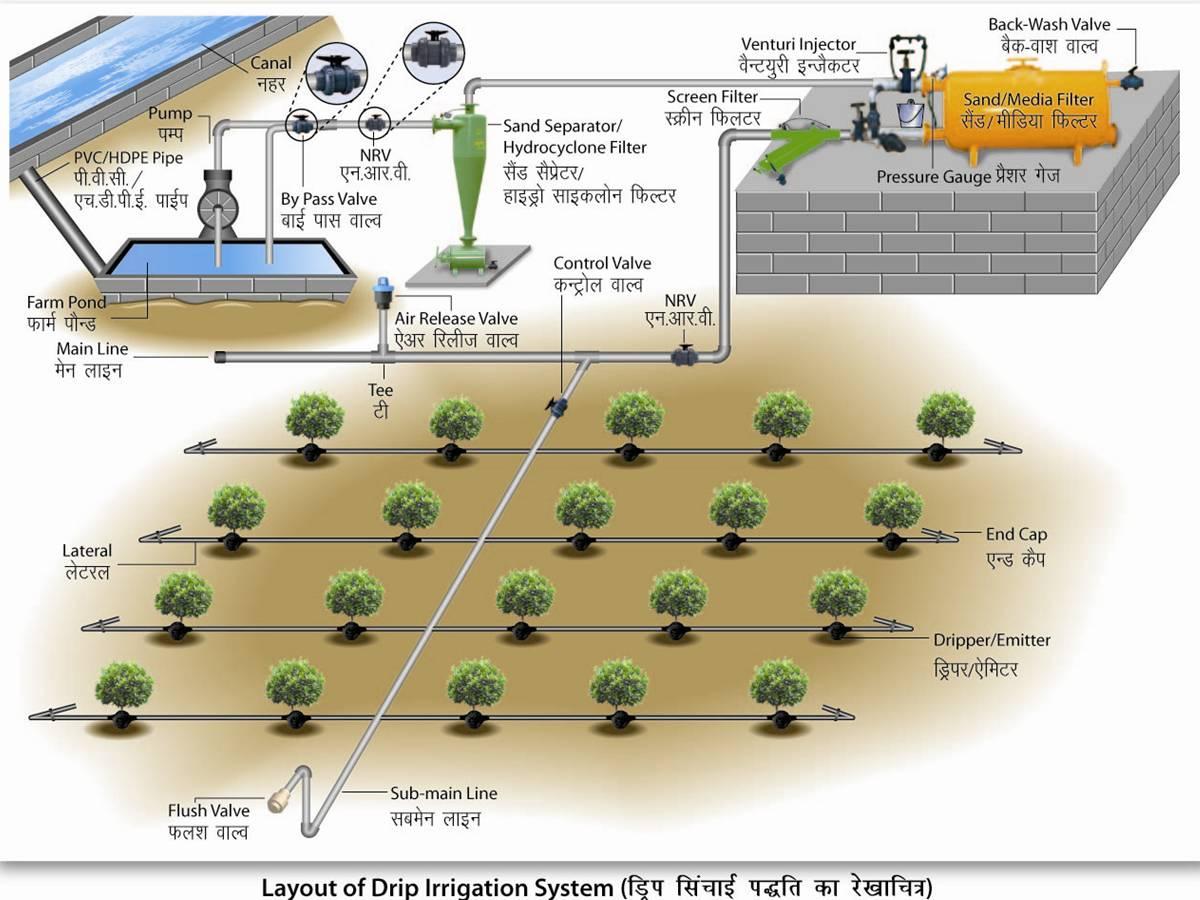
Major Components of Drip Irrigation System
- Pump station takes water from the source and provides the right pressure for delivery into the pipe system.
- Control valves control the discharge and pressure in the entire system.
- Filtration system cleans the water. Common types of filter include screen filters and graded sand filters which remove fine material suspended in the water.
- Fertilizer tank/venturi slowly add a measured dose of fertilizer into the water during irrigation. This is one of the major advantages of drip irrigation over other methods.
- Mainlines, submains and laterals supply water from the control head into the fields. They are usually made from PVC or polyethylene hose and should be buried below ground because they easily degrade when exposed to direct solar radiation. Lateral pipes are usually 13-32 mm diameter.
- Emitters or drippers are devices used to control the discharge of water from the lateral to the plants. They are usually spaced more than 1 metre apart with one or more emitters used for a single plant such as a tree. For row crops more closely spaced emitters may be used to wet a strip of soil. Many different emitter designs have been produced in recent years. The basis of design is to produce an emitter which will provide a specified constant discharge which does not vary much with pressure changes, and does not block easily.
- By-pass assembly
- Pressure gauge
- Micro tubes
Wetting pattern in drip irrigation
Unlike surface and sprinkler irrigation, drip irrigation only wets part of the soil root zone. This may be as, low as 30% of the volume of soil wetted by the other methods. The wetting patterns which develop from dripping water onto the soil depend on discharge and soil type. Figure 64 shows the effect of changes in discharge on two different soil types, namely sand and clay.
Wetting pattern in Sandy Soils
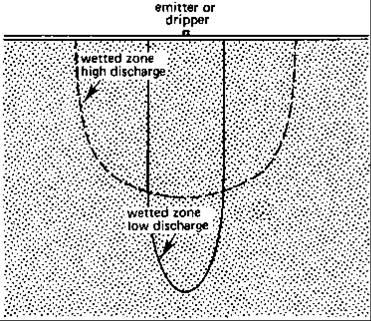
Wetting pattern in Clay Soils
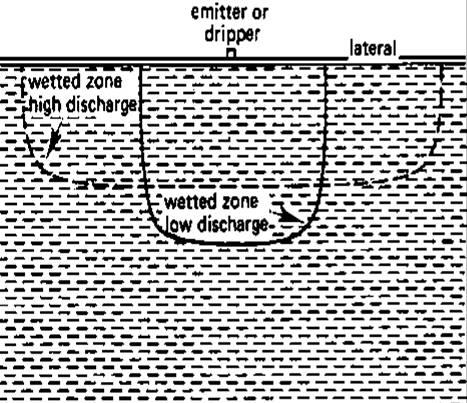
Although only part of the root zone is wetted it is still important to meet the full water needs of the crop. It is sometimes thought that drip irrigation saves water by reducing the amount used by the crop. This is not true. Crop water use is not changed by the method of applying water. Crops just require the right amount for good growth.
The water savings that can be made using drip irrigation are the reductions in deep percolation, in surface runoff and in evaporation from the soil. These savings, it must be remembered, depend as much on the user of the equipment as on the equipment itself.
Drip irrigation is not a substitute for other proven methods of irrigation. It is just another way of applying water. It is best suited to areas where water quality is marginal, land is steeply sloping or undulating and of poor quality, where water or labour are expensive, or where high value crops require frequent water applications.
Crops suitable for Drip Irrigation System
|
1. |
Orchard Crops |
Grapes, Banana, Pomegranate, Orange, Citrus, Mango, Lemon, Custard Apple, Sapota, Guava, Pineapple, Coconut, Cashewnut, Papaya, Aonla, Litchi, Watermelon, Muskmelon etc. |
|
2. |
Vegetables |
Tomato, Chilly, Capsicum, Cabbage, Cauliflower, Onion, Okra, Brinjal, Bitter Gourd, Ridge Gourd, Cucumber, Peas, Spinach, Pumpkin etc. |
|
3. |
Cash Crops |
Sugarcane, Cotton. Arecanut, Strawberry etc. |
|
4. |
Flowers |
Rose, Carnation, Gerbera, Anthurium, Orchids, Jasmine, Dahilia, Marigold etc. |
|
5. |
Plantation |
Tea, Rubber, Coffee, Coconut etc. |
|
6. |
Spices |
Turmeric, Cloves, Mint etc, |
|
7. |
Oil Seed |
Sunflower, Oil palm, Groundnut etc. |
|
8. |
Forest Crops |
Teakwood, Bamboo etc. |
Response of different crops to Drip Irrigation System
|
Crops |
Water saving (%) |
Increase in yield (%) |
|
Banana |
45 |
52 |
|
Cauliflower |
68 |
70 |
|
Chilly |
68 |
28 |
|
Cucumber |
56 |
48 |
|
Grapes |
48 |
23 |
|
Ground nut |
40 |
152 |
|
Pomegranate |
45 |
45 |
|
Sugarcane |
50 |
99 |
|
Sweet lime |
61 |
50 |
|
Tomato |
42 |
60 |
|
Watermelon |
66 |
19 |
Benefits of drip Irrigation
- Increase in yield up to 230 %.
- Saves water up to 70% compare to flood irrigation. More land can be irrigated with the water thus saved.
- Crop grows consistently, healthier and matures fast.
- Early maturity results in higher and faster returns on investment.
- Fertilizer use efficiency increases by 30%.
- Cost of fertilizers, inter-culturing and labour use gets reduced.
- Fertilizer and Chemical Treatment can be given through Micro Irrigation System itself.
- Undulating terrains, Saline, Water logged, Sandy & Hilly lands can also be brought under productive cultivation.
Water conservation through drip
Water is conserved in the following ways:
- Drip irrigation application uniformity is very high, usually over 90%.
- Unlike sprinklers, drip irrigation applies water directly to the soil, eliminating water loss from wind.
- Application rates are low so water may be spoon fed to the crop or plant root zone in the exact amounts required (even on a daily or hourly basis). In contrast, other methods entail higher water application quantities and less frequency. If young plants need water frequently, much of the water applied is often wasted to deep percolation or runoff.
- Low application rates are less likely to run off from heavier soils or sloping terrain.
- Drip irrigation does not water non-targeted areas such as furrows and roads in agriculture, between beds, blocks or benches in greenhouses, or hardscape, buildings or roads in landscape.
- Drip irrigation easily adapts to odd-shaped planting areas which are difficult to address with sprinklers or gravity irrigation.
- Drip irrigation is capable of germinating seeds and setting transplants which eliminates the need for "sprinklering up" and eliminates the resulting waste in the early stages of crop growth.
Drip irrigation is today's need because Water - nature's gift to mankind is not unlimited and free forever. World water resources are fast diminishing.
Source: National Committee on Plasticulture Application in Horticulture, FAO corporate Documentary Repositary, Jain Irrigation Systems Ltd
Bamboo drip irrigation system
Dating back 200 years, tribes in northeast India have used bamboo drip irrigation as a means of bringing water to seasonal crops. This timeless and traditional technology uses locally available material while harnessing the forces of gravity. An assortment of holed bamboo shoots zig-zag downhill, diverting the natural flow of streams and springs across terraced cropland. The advantages of using bamboo are two-fold: it prevents leakage, increasing crop yield with less water, and makes use of natural, local, and inexpensive material.
The Jaintia, Khasi, and Garo hills of Meghalaya are largely made up of steep slopes and generally rocky terrain where the soil has low water retention capacity and where the use of groundwater channels is impossible. During the dry seasons, rainfed crops such as paddy, betal leaf, and black peppers can be irrigated by bamboo drip irrigation.
Within the Jainta hills, the small village of Nongbah relies on terrace agriculture for paddy cultivation. There are no restrictions for individuals tapping into water flows from perennial streams, natural springs, or collection ponds. This enables farmers, nearly 97% of the population, to cultivate paddy, betal leaf, and black peppers in seasonal rotations. Meanwhile, drinking needs are met by perennial springs during the dry months, from October to March.
Only during the winter is irrigation required, and the bamboo system is used for crops that need relatively less water.
The few materials needed are a small dao (a type of local axe), bamboo strands of various sizes, forked branches, smaller bamboo shoots used for the channel diversions, and two willing laborers. A. Singh, in his book Bamboo Drip Irrigation Systems, investigated its use in Meghalaya and says that two workers can construct a system covering one hectare of land in 15 days. About four or five stages of irrigation zig-zag from the water source to the last point of application. Along the way, 18-20 liters of water will eventually disseminate at a rate of 20-80 drops per minute.
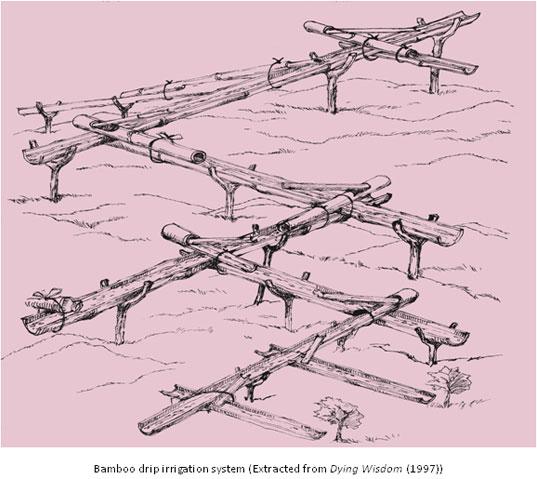
Photo source: Centre for Science and Environment
To get started, locate an available water source. Next, select a sloped area of land (at least 30 meters in variation). Then slice the bamboo shoots and forked branches, placing the wider shoots in the first channel and the smaller pipes for the last section (plan for 5 stages). Puncture a series of holes in the shoots, spacing them equally. Ground clearance should progressively descend so that the water may be dropped near the roots of plants in the last section (10-15 cm above ground). To reinforce the structure, tie the pipes and forked branches together using fiber-rich twine as rope. At points of diversion, smaller bamboo shoots may be used to redirect water.
Materials used during installation last around three years, while maintenance is limited to cleaning and reinforcement after seasonal monsoons. Cost is also limited to labor, which can be carried out by farmers themselves. This traditional water structure is indeed contextual to location. Such variables include: replenishable supplies of bamboo, upland sources of water, and the presence of traditional terrace agriculture.
Adapting to drier growing seasons, farmers are advised to match irrigation decisions with crop selection. It is suggested that during the June to September season, rice cultivation can be stopped and farmers can opt for crops such as pulses, sunflower, sesame and maize. In areas affected severely by drought, farmers may go for pearl millet, minor millet and forage crops. However, in places where there is water stagnation, they can continue to grow rice.
In the Meghalaya hills there are an estimated 3,108 square kilometers of bamboo forests. In 1990, it was estimated that the total yield of bamboo in the state was 2.09 tons/hectare/year. The 38 different species of bamboo in the region are typically harvested at the community level and loosely managed by the Autonomous District Councils (ADC). Bamboo supplies have recently come under threat from a surge in rodent populations, gregarious flowering, disease, and large-scale extraction. Nonetheless, large-scale conservation and protection plans are underway in Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Mizoram, Tripura, and Sikkim, which together contain over 50% of India’s bamboo supply (within 226,000 square kilometers of land.)
The Jaintia, Khasi, and Garo hill tribes have long entrusted the use of bamboo drip irrigation as a means to fulfilling domestic, agricultural, and customary needs. Its function remains unspoiled so as the rains continue to fall and the bamboo continues to grow.
Source: cseindia.org
Last Modified : 3/8/2024
