Rice gall midge management
Rice gall midge management
Rice gall midge
Scientific Name : Orseolia oryzae Wood-Mason
Rice gall midge is a pest of paddy crop, causes a tubular gall at the base of tillers, causing elongation of leaf sheaths called onion leaf or silver shoot. The population density of the rice gall midge is favored mainly by cloudy or rainy weather.

Symptoms of damage
- Maggot feeds at the base of the growing shoot
- Causing formation of a tube like gall that is similar to “onion leaf” or “Silver-shoot”.
- Infested tillers produce no panicles.
Identification of insect pest
- Egg: The fly lays elongate, cylindrical, shinning white or red or pinkish eggs singly or in clusters (2-6) at the base of the leaves.
- Larva: Maggot is 1 mm long after hatching with pointed anterior end. It creeps down the sheath and enters the growing bud. An oval chamber is formed round the site of feeding.

- Pupa: At the time of emergence the pupa wriggles up the tube with the help of antennal horn to the tip of the silver shoot and projects half way out.
- Adult: fly is yellowish brown and mosquito like. The male is ash grey in colour. Adults feed on dewdrops.
Economic Threshold Level
Early to late tillering : 1 gall / m2 or 10 % silver shoot
IPM strategies
The following practices of IPM strategies may be followed for management of Gall midge infestation in Paddy crop:</p.
- Practice early ploughing immediately after harvest of the paddy crop.
- Planting of early maturing resistant/ tolerant varieties may help to avoid high infestations.
- Plough ratoon of the previous crop and remove all off-season plant hosts (grassy weeds and wild rice) from surrounding areas can reduce gall midge incidence.
- Conserve natural enemies: platygasterid, eupelmid, and pteromalid wasps (parasitize the larvae), phytoseiid mites (feed on eggs) and spiders (feed on adults).
- Using only moderate amounts of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers and adopting split applications to reduce population growth rates.
- Avoiding staggered planting (complete trans-planting in an arca within 3 weeks) to reduce infestation.
- Draining out water from paddy fields for 5-7 days will drastically bring down Gall midge population.
- The Gall midge adults are found to be active between dusk time (6 to 10 PM) and hence light traps @ 1 No. Per acre can be operated between 6 to 10 PM to attract Gall midge adults.
- In the event of severe infestation of Gall midge, application of any of the plant based products like l0% Neem leaf extract, 5% NSKE, 1% Neem oil, 0.3 % Fish oil resin soap, 3 % Dasagavya and 3 % Herbal plant extraction can be sprayed to bring down the pest population.
- Collect and destroy infested crop debris.
- Maintain field sanitation.
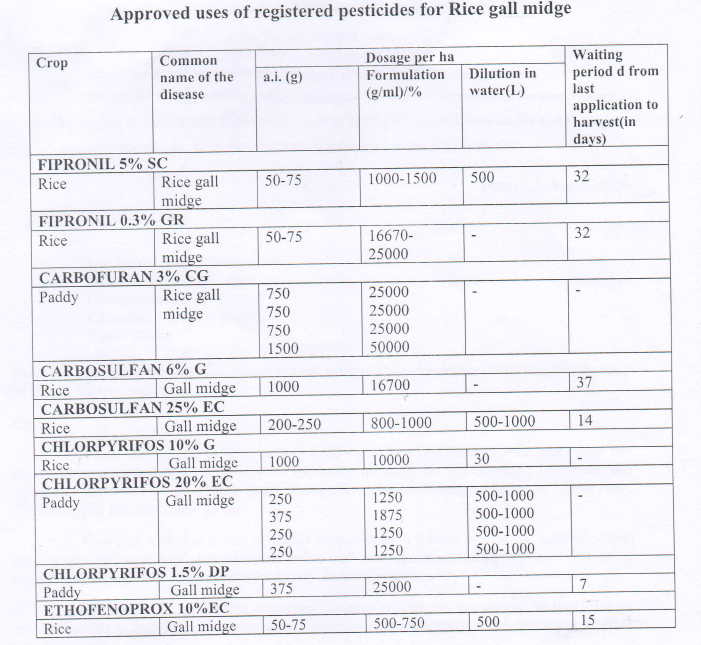
- Insecticides must be used as per label claim approved by the Central Insecticide Board and Registration Committee (CIB&RC). Detailed information is available at http://ppqs.goiirVdivisions/cibrc/major-uses-of-pesticides.
- Use only recommended doses of fertilizers and Insecticides as per approved label claims by CIB&RC.
IPM for Rice
To read the IPM package of practices for Rice, click here.
Source : Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine and Storage
Last Modified : 5/3/2021
© C–DAC.All content appearing on the vikaspedia portal is through collaborative effort of vikaspedia and its partners.We encourage you to use and share the content in a respectful and fair manner. Please leave all source links intact and adhere to applicable copyright and intellectual property guidelines and laws.
RELATED ITEMS
