Nutritional Deficiencies of Tobacco
Nutritional Deficiencies of Tobacco
Nitrogen
 Leaves become yellowish (chlorotic) starting from lower leaves and move upward as the deficiency increases. N deficient plants are stunted leaves are smaller and more upright than normal plants.
Leaves become yellowish (chlorotic) starting from lower leaves and move upward as the deficiency increases. N deficient plants are stunted leaves are smaller and more upright than normal plants.
Phosphorus
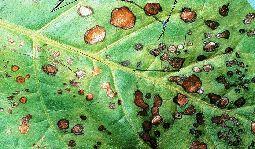 Slow and stunted growth, maturity delayed Leaf colour becomes dark green. Mid-day wilting and brown spots on leaves may be observed under mild P deficiency.
Slow and stunted growth, maturity delayed Leaf colour becomes dark green. Mid-day wilting and brown spots on leaves may be observed under mild P deficiency.
Potassium
 Since potassium is very mobile within the plant, symptoms appear first on lower leaves. Older leaves become yellow and necrotic. Mottled or scorched appearance develops at the tips and along the margins of leaves. The plants are less stunted as compared to P & N deficiency.
Since potassium is very mobile within the plant, symptoms appear first on lower leaves. Older leaves become yellow and necrotic. Mottled or scorched appearance develops at the tips and along the margins of leaves. The plants are less stunted as compared to P & N deficiency.
Calcium
 Calcium deficiency in tobacco occurs in sandy soil with low pH conditions. As the Ca is immobile in plant, the symptoms first appear on the youngest leaves or buds. Younger leaves develop pale green colour followed by rolling and downward curling. Under extreme deficiency, terminal bud dies while lower leaves develop darker colour.
Calcium deficiency in tobacco occurs in sandy soil with low pH conditions. As the Ca is immobile in plant, the symptoms first appear on the youngest leaves or buds. Younger leaves develop pale green colour followed by rolling and downward curling. Under extreme deficiency, terminal bud dies while lower leaves develop darker colour.
IPM for Tobacco
To know the IPM practices for Tobacco, click here.
Source: NIPHM and Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine & Storage
Last Modified : 2/13/2020
This topic covers information about Nutrient Defic...
This topic covers the information related to Nutri...
This topic covers information about Cabbage and Ca...
This topic covers the information related to Nutri...
