Mustard: Diseases and Symptoms
Mustard: Diseases and Symptoms
Alternaria blight
Disease symptoms The disease attacks on the lower leaves as small circular brown necrotic spots which slowly increase in size.
The disease attacks on the lower leaves as small circular brown necrotic spots which slowly increase in size.- Many concentric spots coalesce to cover large patches showing blightening and defoliation in severe cases.
- Circular to linear, dark brown lesions also develop on stems and pods, which are elongated at later stage.
- Infected pods produce small, discolored and shriveled seeds.
- The disease is externally and internally seed born.
- The pathogen survives through spores (conidia) or mycelium in diseased plant debris or weed.
- Moist (more than 70% relative humidity) coupled with warm weather (12-25 °C ) and intermittent rains favours disease development
White rust
Disease symptoms- Both local and systemic infections are observed.
- In case of local infection, white creamy yellow raised pustules appear on the leaves which later coalesce to form patches.
- In systemic infection and during humid weather, mixed infection of white rust and downy mildew cause swelling and distortion of the stem and floral parts due to hypertrophy and hyperplasia and develop “stag head” structure.

- The pathogen survives through oospores in affected host tissues and soil.
- Secondary infection is carried out by sporangia and zoospores which produce new infection.
- Moist (more than 70% relative humidity) coupled with warm weather (12-25 °C) and intermittent rains favours disease development.
Downy mildew
Disease symptoms- Grayish white irregular necrotic patches develop on the lower surface of leaves.
- Later under favourable conditions brownish white fungal growth may also be seen on the spots.
- The most conspicuous and pronounced symptom is the infection of inflorescence causing hypertrophy of the peduncle of inflorescence and develop stag head structure.

- The pathogen survives as oospores on the affected plant tissues in soil and on weed hosts.
- Atmospheric temperature in the range of 10-20 °C and relative humidity>90% RH favours disease development
Powdery mildew
Disease symptoms Symptoms appear as dirty white, circular, floury patches on either sides of the leaves.
Symptoms appear as dirty white, circular, floury patches on either sides of the leaves.- Under favourable environmental conditions, entire leaves, stems, floral parts and pods are affected.
- The whole leaf may be covered with powdery mass.
- The pathogen survives through cleistothecia present in the crop debris in the field.
- High temperature (15-28 ºC) coupled with low humidity (<60% humidity) and low or no rainfall with wind favours disease development.
Bacterial blight/ black rot
Disease symptoms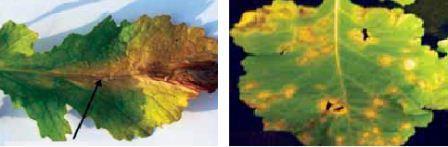 The leaf tissue turns yellow and chlorosis reach towards the centre of the leaf and form V shaped area with base of V towards the midrib. The veins show brown to black discoloration. Dark coloured streaks are formed on the stem from the ground level and gradually these streaks enlarge and girdle the stem.
The leaf tissue turns yellow and chlorosis reach towards the centre of the leaf and form V shaped area with base of V towards the midrib. The veins show brown to black discoloration. Dark coloured streaks are formed on the stem from the ground level and gradually these streaks enlarge and girdle the stem.- Stem become hollow due to internal rotting.
- Midrib cracking of lower leaves, browning of veins and withering is observed.
- In severe cases, the vesicular bundles of the stem also turn brown and the plant collapses.
- The pathogen survives in infected plant residue in soil and seed.
- The pathogen spreads by soil and irrigation water.
- Warm and humid climate favours the disease development
Club root
Disease symptoms Affected plants remain stunted.
Affected plants remain stunted.- Tiny nodules to large club shaped outgrowths develop in root system.
- Leaves turn pale green or yellow followed by wilting and under severe conditions the plants die
- The pathogen survives in the soil as resting spores and these spores act as primary source of inoculum.
- Humid weather and high soil moisture favour disease development.
Sclerotinia stem rot
Disease symptoms Elongated water soaked lesions appear on stem near to the crown region, covered with cottony mycelial growth later on.
Elongated water soaked lesions appear on stem near to the crown region, covered with cottony mycelial growth later on.- Plant looks like whitish from distance at internodes or base.
- Premature ripening and shredding of stem, wilting and drying.
- Brown to black sclerotial bodies may also be seen in the later stage on the infected plant parts.
- The pathogen survives as mycelium in dead or live plants and as sclerotia in infected plant parts or on the soil surface or with seed as contaminant.
- High humidity (90-95%) and average temperature (18-25 oC) along with wind current favours the disease development.
IPM for Mustard
To know the IPM practices for Mustard, click here.
Source: NIPHM and Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine & Storage
Last Modified : 12/15/2019
© C–DAC.All content appearing on the vikaspedia portal is through collaborative effort of vikaspedia and its partners.We encourage you to use and share the content in a respectful and fair manner. Please leave all source links intact and adhere to applicable copyright and intellectual property guidelines and laws.
RELATED ITEMS
Clusterbean
This topic explains about Improved Cultivation Pra...
Chilli Diseases
This topic covers information about Chilli Disease...
Ber Diseases
This topic covers information about Ber Diseases.
Apple: Diseases and Symptoms
This topic covers the Information related to Disea...
