Safflower: Diseases and Symptoms
Safflower: Diseases and Symptoms
Alternaria blight
Disease symptoms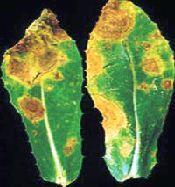 It is the most destructive disease.
It is the most destructive disease.- Dark necrotic lesions 2-5 mm in diameter are formed first on hypocotyls and cotyledons.
- In mature plants, small brown to dark brown concentric spots of 1-2 mm appear on leaves.
- Symptoms also appear on stem and severely infected plant gets blighted.
- Brown discolouration appears on the stem, dark brown spots with concentric rings up to 1 cm in diameter appear on the leaves which later develop into large lesions.
- Seeds also may be affected. Dark sunken lesions are produced on the testa. It may rot and damping off of seedlings occur.
- The disease is externally and internally seed borne. The pathogen survives through spores (conidia) or mycelium in diseased plant debris or weed.
- Moist (more than 70% relative humidity) and warm weather (12-25 ºC) and intermittent rains favours disease development.
Cercospora leaf spot
Disease symptoms Safflower plants few weeks after planting or at flowering stage are commonly attacked.
Safflower plants few weeks after planting or at flowering stage are commonly attacked.- Circular to irregular brown sunken spots of 3-10 mm diameter are formed on leaves.
- Spots are surrounded by yellow halos.
- Symptoms first appear on lower leaves and spread to upper leaves.
- Stems and nodes may also be affected.
- In severe infections bracts are also affected with reddish brown spots.
- Affected flower buds turn brown and die.
- The fungus survives in seed and affected plant debris and spreads through wind borne spores.
- Warm humid weather favours the disease development.
Powdery mildew
Disease symptoms

- The disease is characterized by whitish powdery growth on leaves
- Later the fungus spreads over the entire leaf. Leaves turn yellow and dry up
- The pathogen survives as oospores on the affected plant tissues and on weed hosts
- Cool (10-20ºC) and wet weather (90% RH) favours disease development
Head rot and wilt
Disease symptoms- Plants become yellowish, turn brown and ultimately die
- Large black sclerotia of the fungus are formed on the crown inside the stem, floral heads and adjoining roots
- Shredding of the stem takes place
Mosaic
Disease symptoms In CMV infected safflower plants young leaves show irregular yellow or light patches alternating with normal green areas.
In CMV infected safflower plants young leaves show irregular yellow or light patches alternating with normal green areas.- Leaves may become blistered and distorted and infected plants are stunted.
- In few plants primary leaves are produced, forming a rosette of leaves exhibiting mosaic mottling and from the centre of this, the axis bearing secondary leaves are produced.
- The disease is transmitted in semi persistent manner by aphid Aphis gossypii.
- Aphids are more active in warm summer conditions and increased their population as well as spread the viruses more.
Ramularia leaf spot
Disease symptoms Round and irregular spots of 100 mm or more in diameter occur on both sides of leaves
Round and irregular spots of 100 mm or more in diameter occur on both sides of leaves- Whitish dense mass of conidia remain at the center which reflects light, dry spots are brown in color.
Rust
Disease symptoms Seedling infection causes twisting towards one side
Seedling infection causes twisting towards one side- Chesnut brown postules are formed on hypocotyl leading to collapse of seedling
- On older plants girdling and hypertrophy of the stem base may occur
- Small powdery chesnut brown postules of 1-2 mm in size develop on leaf surface which later turn black.
Wilt
Disease symptoms Yellowing of leaves on one side of plant starts particularly from lower leaves followed by wilting the progresses upwards
Yellowing of leaves on one side of plant starts particularly from lower leaves followed by wilting the progresses upwards- Lesion at soil line is first symptom noticed which extends inside and affects the vascular system
- Plant starts to wilt, drooping more often
- Infected heads have aborted seed.
Root rot
Disease symptoms Dark cortical lesions occur slightly below or at the soil level on the stem, which later extend upwards
Dark cortical lesions occur slightly below or at the soil level on the stem, which later extend upwards- Lesions frequently girdle the stem
- Root development is reduced and finally seedlings die
IPM for Safflower
To know the IPM practices for Safflower, click here.
Source: NIPHM and Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine & Storage
Last Modified : 2/13/2020
© C–DAC.All content appearing on the vikaspedia portal is through collaborative effort of vikaspedia and its partners.We encourage you to use and share the content in a respectful and fair manner. Please leave all source links intact and adhere to applicable copyright and intellectual property guidelines and laws.
RELATED ITEMS
Safflower: Insect pests Management
This topic covers the information related to Insec...
Safflower: Natural Enemies
Natural enemies of Safflower insect pests are cove...
Safflower: Crop Stage-wise IPM
This topic covers the Information related to Crop ...
Safflower Pests
This topic covers the information related to Pest ...
