Cabbage and Cauliflower diseases
Cabbage and Cauliflower diseases
Damping Off
Pythium aphinidermatum (Eds.) Fitz.; Rhizoctonia sonali Kuhn
Symptoms:
- Damping off of Cabbage occurs in two stages, i.e. the pre-emergence and the post-emergence phase.
- In the pre-emergence the phase the seedlings are killed just before they reach the soil surface.
- The young radical and the plumule are killed and there is complete rotting of the seedlings.
- The post-emergence phase is characterized by the infection of the young, juvenile tissues of the collar at the ground level.
- The infected tissues become soft and water soaked. The seedlings topple over or collapse.

Favourable Conditions:
- High humidity, high soil moisture, cloudiness and low temperatures below 24° C for few days are ideal for infection and development of disease.
- Crowded seedlings, dampness due to high rainfall, poor drainage and excess of soil solutes hamper plant growth and increase the pathogenic damping-off.
Survival and spread:
- Primary: Soil, Seed, Water
- Secondary: Conidia through rain splash or wind

Club root of crucifers
Also known as Finger and toe disease: Plasmodiophora brassicae Woronin
Symptoms:
- Stunting and yellowing of plants
- Leaves become yellowish and wilt on hot days.
- Club like swelling of root and root lets
- Club root is particularly prevalent on soils with a pH below 7, whereas it has been observed that the disease is often less serious on heavy soils and on soils containing little organic matter

Survival and spread:
- Primary: Soil borne resting spores, which survive for longer periods in soil (10yrs.) Collateral hosts: Broccoli, Brussels sprout, cabbage, cauliflower, Chinese cabbage, mustard, raddish, turnip
- Secondary: Resting spores or zoospores carried through irrigation water or by root contact.
Favourable conditions:
- It occur at a temp range of 12 - 270C (250C)
- High soil moisture
- Neutral to acidic soils 5-7.0 pH
Alternaria leaf spot
Alternaria brassicae (Berk.) Sacc; A. brassicicola (Schw.) Wiltshire
Common on cabbage, cauliflower and mustard.
Symptoms:
- Spots are small, dark coloured
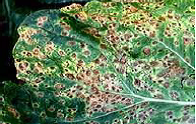
- They enlarge, soon become circular & 1mm. in diameter
- Under humid conditions groups of conidiophores will be formed in the spot
- Spots develop concentric rings
- Finally the spots coalesce leading to blighting of leaves.
- The fungus is seed borne and cause shriveling of seeds and poor germination
- Linear spots also appear on petioles, stems, pods & seeds
Survival and spread:
- Primary: Mycelium persisting in the seed or as spores on seed or from debris
- Secondary: Wind or insect borne conidia
Favourable conditions:
- Soil temperature of around 280 C
- High humidity or persistent dew
- Moist weather with intermittent showers>
Black rot
Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris (Dowson) Dye, et al.
Serious on cabbage, cauliflower, knol-khol and raddish
Symptoms:
- First appear as chlorotic or yellow (angular) areas near the leaf margins
- Yellow area extends to veins and midrib forming characteristic ‘v’ shaped chlorotic spots which later turn black
- Veins and veinlets turn brown and finally black
- Vascular blackening extend beyond affected veins to midrib, petiole and stem
- In advanced stages, infection may reach the roots system and blackening of vascular bundles occurs. Bacterial ooze can also be seen on affected parts
- If the infection is early, the plants wilt and die
- If the infection is late plants succumb to soft rot and die.

Survival and spread:
- Primary :Bacterial cells internally seed borne and soil borne
- Secondary: Bacterial cells dispersed through irrigation water and rain splashes.
Favourable conditions:
- Relative humidity > 90%
- High soil moisture
- Frequent rains
Downy Mildew
Peronospora parasitica (Pers.) Fr. Syno. (Hyaloperonospora parasitica (Pers.) Constant., 2002
Severe in raddish, cabbage, cauliflower, mustard, and knol-khol.
Symptoms:
- Small purplish brown spots on under surface of leaves
- Small, pale yellow angular spots on upper surface of leaves, with downy growth on the under surface. The spots coalesce and the leaves shrivel and dries up prematurely
- In cabbage, these spots expose the heads to soft rot
- Cauliflower curds look brownish at the t
- Stems show dark brown and depressed lesions or streaks which later develop downy growth of fungus.

Survival and spread:
- Primary: Oospores in infected plant debris or in soil
- Secondary: Wind borne and rain splashed sporangia
Favourable conditions:
- It occur at a moderate temperature range of 12-270 C
- High soil moisture
- Neutral to acidic soils 5-7.0 pH
Powdery mildew
Erysiphe cruciferarum Opiz.ex Junnell
Infects mostly cabbage and cauliflower
Symptoms:
- White powdery spots on the upper surface of leaves, stems,

- flower parts etc.
- Finally the mildew may cover the entire surface
- Infected plants may show rotting and do not have normal growth
Survival and spread:
- Primary: Dormant mycelium in infected plant debris
- Secondary: Wind borne conidia.
Favourable conditions:
- It occur at a moderate temperature range of 12-270 C
- Dry conditions with morning relative humidity of 80%
White rust
Albugo candida (Pers. ex Lév.) Ktze
Symptoms:
- White, shiny raised blisters (pustules) on the lower surfaces of leaves, stems and flowers
- Pustules coalesce to form irregular patches
- The epidermis ruptures exposing white spore mass which gives the pustule a powdery appearance
- Distortion of the floral parts including petals, pistils and anthers due to hypertrophy and Hyperplasia
- Plants malformed beyond recognition

Survival and spread:
- Primary: Oospores in soil and sporangia from perennial weed hosts in the vicinity
- Secondary: Wind borne and rain splashed conidia (sporangia) or autonomous zoospores
Favourable conditions:
- Relative humidity > 90%
- High soil moisture
- Frequent rains
IPM for Cabbage and Cauliflower
To know the IPM practices for Cabbage & Cauliflower, click here.
Source: NIPHM, Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine & Storage
Last Modified : 2/14/2023
This topic covers information about Chilli Disease...
This topic covers the Information related to Disea...
This topic covers information about Ber Diseases.
This topic explains about Improved Cultivation Pra...
