Curryleaf Pests and Diseases
Curryleaf Pests and Diseases
Leaf spot

Phyllosticta leaf spot symptoms range from a few round spots or lesions. It may cause early loss of leaves in case of severe infestation and can debilitate the tree. The irregular, round, yellowish brown lesions are produced on leaves. Under the favourable conditions, tiny black fruiting bodies of the pathogen are produced, usually they form a circle. The center of these spots is dead tissue that easily breaks away leaving a hole.
Primary infection: Through soil and rain splash
Secondary infection : through air and rain splash during wed condition
Tortoise beetle
Biology
- Grub: Black with a forked posterior and a flattened body.
- Adults: Reddish-brown beetles.
Life cycle:
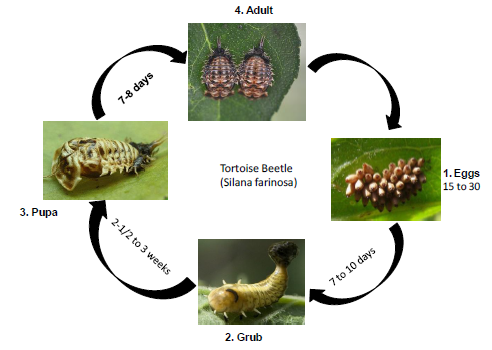
Damage Symptoms:
Cause heavy defoliation of commercial crops. Both the adult beetle and the grub feed on the leaves, boring holes into them.
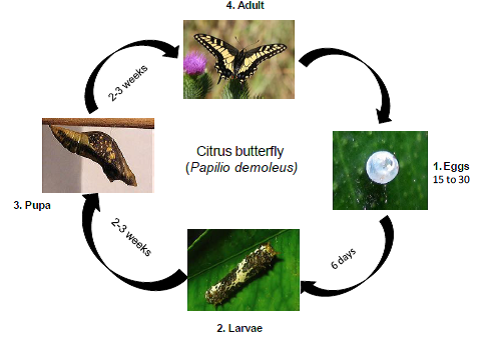
Citrus butterfly
Biology:
- Eggs: Yellowish white, round, smooth eggs are laid singly on tender leaves and shoots by P. demoleus. Egg hatches in about 3 – 8 days.
- Larva: Freshly hatched caterpillars are dark brown and soon develop irregular white markings on their body resembling bird’s drop. The caterpillars feed voraciously on tender leaves right up to the mid ribs and defoliate the entire seedlings or the tree leaving behind the only midribs.
- Adults: Papilio demoleus is a big beautiful butterfly with yellow and black markings on all the four wings, having wing expanse of about 50-60 mm. Its hind wings have a brick red oval patch near the anal margin and there is no tail like extension behind though common in Papilionidae. Papilio polytes males are black and females vary in form. Papilio helenus has black wings with three white distal spots.
Life cycle:
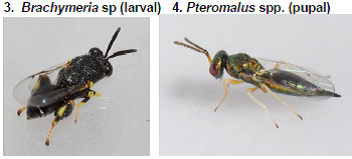
Natural enemies : Parasitoids

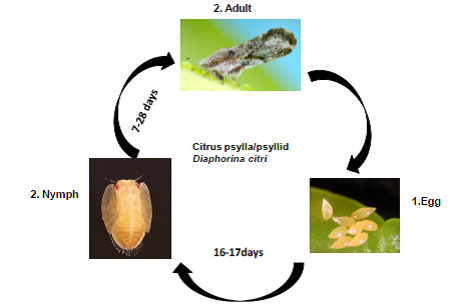
Citrus psylla/psyllid
Biology:
- Nymphs: Its nymphs are yellow, orange or brown with flattened bodies. They are hard to see, since they're only 1/100 to 1/14 inch long. The nymphs also secrete a sticky substance called honeydew that attracts sooty mold.
- Adults: Citrus psyllid is a tiny, mottled-brown, winged insect that damages curry leaf plants when it sucks sap out of young leaves. This psyllid grows to be between 1/16 and 1/8 inch long with red eyes and short antennae.
Life cycle:
Damage symptoms:
Citrus psyllids are mottled brown insects that feed directly on the leaf of the curry leaf tree. This causes damage to the leaves and stems, and can also introduce bacteria to the tree. Symptoms include twisted and curling leaves, and dieback of shoots.
Natural enemies - Predators:

Scales
Scales are tiny insects that appear as small, flat bumps on the surface of a leaf.
Life cycle:
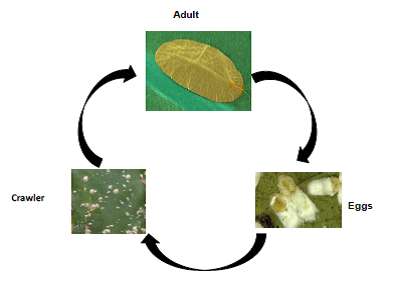
Nature and symptoms of damage:
Scales damage plants by sucking out plant sap as a result leaves to yellow and wilt. While a few scales will not damage a curry tree, this insect reproduces rapidly and a small population can quickly become an infestation. Close monitoring of your curry tree can also help to catch scale problems before they become infestations.
Natural enemiesParasitoids:

Predators:

Mealybugs
Biology:
Citrus mealy bugs are soft pinkish-white insects with a waxy appearance. Mealy bugs are softbodied, wingless insects that grow between 1/20 and 1/5 inch long. Mealy bugs lay large clusters of several hundred eggs on the surface of a leaf, which then hatch into yellow nymphs, which feed on plant sap.
Life cycle:
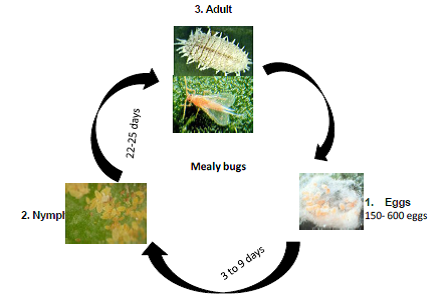
Damage symptoms:
In addition to causing leaves to shrivel, large infestations of citrus mealybugs can cause a tree’s fruit to drop prematurely. Mealybugs usually gather in large numbers, causing premature leaf drop and twig dieback when they feed. Like psyllids, they secrete honeydew, which attracts black sooty mold.
Natural enemiesParasitoids:

Predators:

Aphids
Biology:
Aphids are small pear-shaped insects that may appear in a range of colors, including yellow, green, brown or white.
Life cycle:
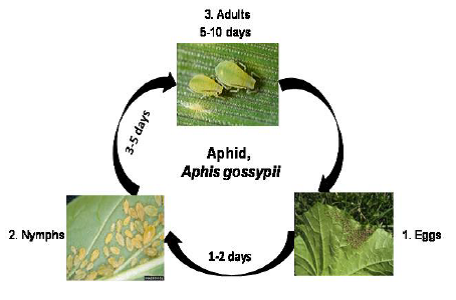
Damage symptoms:
Aphids suck the juices from a plant, causing the leaves to mottle and curl, and can also introduce mold fungus. Aphids tend to feed in dense clusters and are slow to react when disturbed.
Natural enemies
Parasitoids:

Predators:

Two spotted spider mite
Two-spotted mites reproduce sexually, and the females lay eggs on buds, leaves, twigs, stems and trunks. The eggs, which are laid in vast numbers, hatch to produce nymphs which grow through a succession of moults. The first stage nymphs are six-legged; the subsequent stage produces nymphs with a full complement of eight legs. Two-spotted mites overwinter in the soil. Generation time will vary according to temperature, but in warm conditions this time can be as short as four days.
Life cycle:
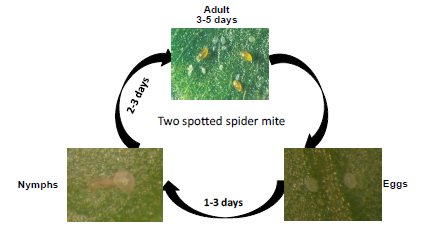
Damage symptoms:
Two spotted spider mite and carmine spider mite damage to strawberries appears as stippling, scarring, and bronzing of the leaves and calyx. damaging during the first 2 to 5 months following transplanting in late summer or fall, and yield loss is detectable at all mite infestation levels exceeding one mite per leaflet
Natural enemies
Predator mites:

IPM for Curry Leaf
To know the IPM practices for Curry Leaf, click here.
Source: NIPHM ; Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine & Storage
Last Modified : 3/23/2020
This topic covers information about Fig Diseases.
This topic covers the Information related to Disea...
This topic covers the information related to disea...
This topic covers the Information related to Disea...
