Moth bean Diseases
Moth bean Diseases
Fusarium wilt
Disease symptoms:
- The first symptom of the disease in the field is drooping of the plants followed by sudden death. The leaves may also turn yellow and drop off prematurely.
- Pod formation is severely affected. In collar regions of the wilted plants, necrosis and discolouration can be seen.
- The diseased plants can be pulled out easily than the healthy ones.
- When the diseased stem is cut, there is a dark brown, discoloured band around the vascular system. Infection occurs directly through the root hairs.
- The fungus survives for indefinite periods in the soil.
Survival and spread:
- This fungal disease may spread through infected plant debris and in seeds.
Favourable conditions:
- Fusarium wilt is more severe during hot, dry weather conditions and particularly when plants are under stress

Charcoal rot or ashy stem blight
Disease symptoms:
- The disease symptom starts as yellowing of lower leaves, followed by drooping and defoliation.
- The stem portion near the ground level shows dark brown lesions and bark at the collar region shows shredding.
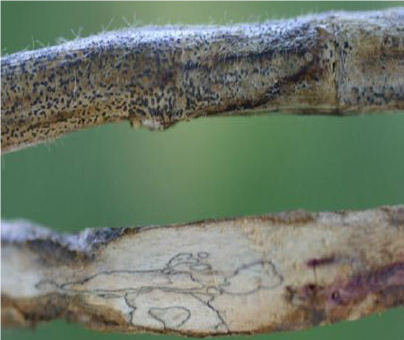
- The sudden death of plants is seen in patches. In the grown-up plants, the stem portion near the soil level shows large number of black pycnidia.
- The stem portion can be easily pulled out leaving the rotten root portion in the soil.
- The infection when spreads to pods, they open prematurely and immature seeds shriveled and become black in colour.
- Minute pycnidia are also seen on the infected pods and seeds.
- The rotten root as well as stem tissues contains a large number of minute black sclerotia on the infected pods and seeds.
Survival and spread:
- M. phaseolina survives as microsclerotia in the soil and on infected plant debris. The microsclerotia serve as the primary source of inoculum and have been found to persist within the soil up to three years.
- Seeds may also carry the fungus in the seed coat.
Favourable conditions:
- Germination of the microsclerotia occurs throughout the growing season when temperatures are between 28 oC and 35oC.
- he rate of infection increases with higher soil temperatures and low soil moisture will further enhance disease severity.
Bacterial leaf spot and blight
Disease symptoms:
- Halo blight occurs primarily when temperatures are cool.
- Light greenish-yellow circles that look like halos form around a brown spot or lesion on the plant. With age, the lesions may join together as the leaf turns yellow and slowly dies.
- Stem lesions appear as long, reddish spots. Leaves infected with common blight turn brown and drop quickly from the plant.

Survival and spread:
- The bacterium survives in the infected plant debris and in seeds.
- The secondary spread is by rain water.
Favourable conditions:
- Rain and damp weather favor disease development.
- Blight occurs primarily when temperatures are cool and moist weather
Mung bean yellow mosaic virus
Disease symptoms:
- The leaves show sharply defined patches of unusual coloration.
- The causal agents of these symptoms may be nutrient imbalance

Survival and spread:
- Virus occurs worldwide in many agricultural crops, ornamentals and weeds. Many of these plants serve as reservoirs for season to season survival of the virus.
- The virus is transmitted by white fly
Cercospora leaf spot
Disease symptoms:
- On infected leaves (especially those more mature) look for brown or rust-coloured lesions that vary from circular to angular, are 2-10 mm, and may coalesce.
- Lesions may have a grey centre with a slightly reddish border.
- Conidia develop at the centre on short conidiophores.
- Severely affected leaves become chlorotic. Lesions may dry and portions may fall out, giving the leaf a shot-hole appearance.
- Lesions and blemishes may occur on branches, stems and pods.
Survival and spread:
- The fungus survives in the infected plant debris and in seeds.
Favourable conditions:
- Rain and damp weather favor disease development.
- Leaf spot occurs primarily when temperature are optimum and moist weather
IPM for Mothbean
To know the IPM practices for Mothbean, click here.
Source: NIPHM; Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine & Storage
Last Modified : 4/1/2020
© C–DAC.All content appearing on the vikaspedia portal is through collaborative effort of vikaspedia and its partners.We encourage you to use and share the content in a respectful and fair manner. Please leave all source links intact and adhere to applicable copyright and intellectual property guidelines and laws.
RELATED ITEMS
Chilli Diseases
This topic covers information about Chilli Disease...
Fenugreek Diseases
This topic covers information about Fenugreek Dis...
Fennel: Diseases and Symptoms
This topic covers the Information related to Disea...
Cucurbitaceous Vegetable Diseases
This topic covers information about Cucurbitaceous...
