Cucurbitaceous Vegetable Insect Pests
Cucurbitaceous Vegetable Insect Pests
Cucurbit fruit fly
It is one of the important pests on gourds like bittergourd, snakegourd, melons, coccinia etc., throughout the country
Biology:
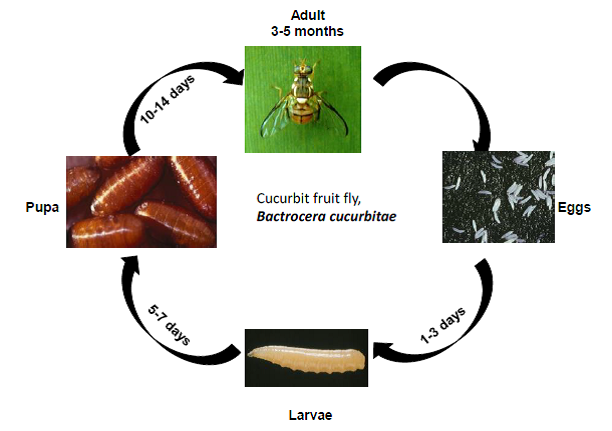
- Egg: The female fly oviposits on soft fruits. Cavity is made by sharp ovipositor and 12 cylindrical eggs are laid in the evening time and exuding gummy substance covers, cements and makes it water proof. Female lays 58-95 eggs in 14-54 days. Egg period is 1-9 days.
- Maggot: The maggots are apodus, acephalous, dirty white, wriggling creatures, thicker at posterior end and tapering at the other to a point. Larval period is 13 days in summer and about three weeks in winter. Mature maggots come out and jump to ground and select suitable place, enter soil and pupate.
- Pupa: Pupa is barrel shaped. Pupal period is 69 days
- Adult: Adult flies emerge from pupa during morning hours and mate at dusk. Adults are reddish brown with lemon yellow markings on thorax with spotted wings. It is active throughout the year. Adults hibernate during winter and they become active in hot weather. Longevity is 14 days.
Life cycle:
Symptoms of damage:
- Only maggots cause damage by feeding near ripe fruits, riddling them and polluting pulp.
- Maggots bore into the fruit and feed on pulp forming lesions.
- Fruits decay due to secondary bacterial infection.
- Damage is more serious in melons. Fruits at early stage also are attacked. Such fruits do not develop. Infestation results in premature drop of fruits.
- Decay of fruits due to secondary bacterial infection
- The damage is more in monsoon season.
Parasitoids:
Opius fletcheri

Predators:
Ants:

Red pumpkin beetles
These insects infest bittergourd, snakegourd, melons, pumpkin, coccinia etc.
Biology:
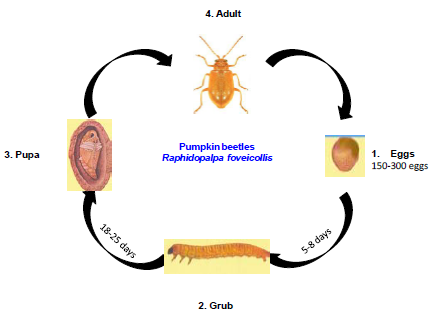
- Egg: Brownish elongate eggs are laid in the soil and each female may lay about 150 to 300 eggs singly or in groups of 8-9 near the base of plants. Egg period is 5-8 days.
- Grub: Grubs are creamy white with darker oval shield at back. Grub period is 13-25 days.
- Pupa: Pupation takes place in an earthen cocoon. Pupal period is 7-17 days.
- Adult: Raphidopalpa foveicollis has reddish brown elytra; A. intermedia has blue black elytra; and A. cincta has grey elytra with black border.
- Total life cycle takes 26-27 days. There are 5 to 8 generations/year.
Life cycle:
Nature and symptoms of damage:
- Beetles are more destructive.
- They bite holes on leaves and also feed on flowers.
- Beetles injure the foliage, flowers and cotyledons by biting holes into them.
- Early sown cucurbits are severely damaged necessitating resowing.
- Beetle damage results in
- Numrous of holes on leaves.
- Grubs after hatching, feed on roots of plants below soil surface.
- Grubs bore into vines, feed on fruits that come in contact with the soil.
Predators:

Parasitoids:

Epilachna beetle/Hadda beetle
Spotted beetles are distributed from East Asia to South Asia and Australia. They are polyphagous and feed predominantly on cucurbits, cucurbits, potato, and kidney beans as well as eggplant. These beetles are considered to be one of the most serious groups of pests damaging eggplant. In addition, they also feed on other Solanaceous plants such as S.nigrum, S.xanthocarpum, S.torvum, Datura sp, Physalis sp and Withania somnifera.
Biology:
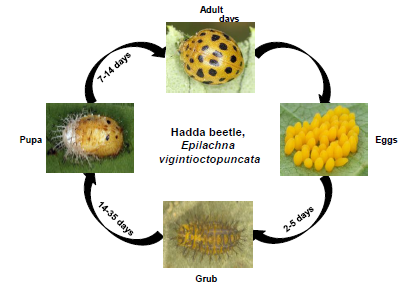
- Egg: The females lay eggs mostly on the lower leaf surfaces. Each female lays about 100-400 eggs. The egg is spindle-shaped and yellowish in color. Eggs are laid in clusters of 10-40. The egg period varies from two to five days
- Grub: The grub is creamy white or yellowish in color with black spiny hairs on the body. The grub period is two to five weeks depending on the temperature. Grubs pupate on the leaves and stem.
- Pupa: The pupa resembles the grub but is mostly darker in color, although it sometimes is yellowish in color. The pupa bears spiny hairs on the posterior, but not the anterior, part of the body. The pupal period is one to two weeks.
- Adult: The subfamily Epilachninae contains plant-feeding ladybird beetles because most other ladybird beetles are predators, not plant pests. These brownish or orange- colored, hemispherical beetles are larger than other ladybird species. E. vigintioctopunctata (in Latin, viginti means 20 and octo means 8) has 28 black spots on the forewing (elytra). E. dodecastigma (dodecam means 12 in Greek) has 12 black spots on the elytra. However, beetles with 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24 or 26 spots have been observed under field conditions, due to mating between females of E. dodecastigma and males of E. vigintioctopunctata.
Life Cycle:
Damage symptoms:
The grub and adult have chewing mouthparts. Hence, they scrape the chlorophyll from the epidermal layers of the leaves. The feeding results in a typical ladder-like window. The windows will dry and drop off, leaving holes in the leaves. In severe infestations, several windows coalesce together and lead to skeletonization i.e. the formation of a papery structure on the leaf.
Parasitoids:

Nematodes:
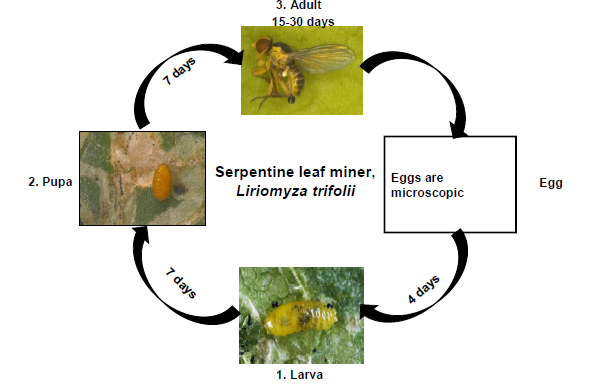
Serpentine leaf miner
Biology:
- Egg: Eggs are minute in size and orange yellow in colour. The egg hatches in 4 days.
- Larva: Apodous maggot feeds on chlorophyll mining in between epidermal layers. Full grown maggot measures 3 mm. Larval duration is about 7 days.
- Pupa: Pupation is in soil. Some pupae are found in leaves. Pupation takes place inside a thin loose mesh of silken cocoon. Pupal period is about 7 days.
- Adult: It is a pale yellowish fly, measuring 1.5 mm in length. The female fly punctures upper surface of leaf to lay eggs singly . Total life cycle takes 3 weeks.
Life cycle:
Damage symptoms:
- Leaves with serpentine mines
- Drying dropping of leaves in severe cases
Favourable conditions:
Warm weather conditions are favourable for multiplication.
Mining on leaves

Parasitoids:

Predators:

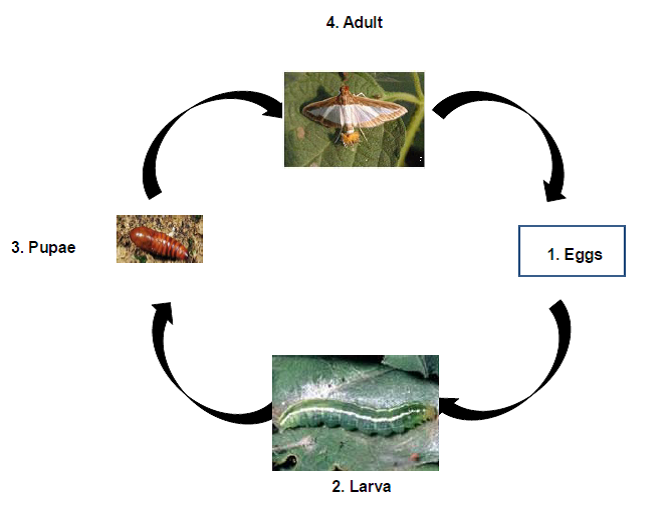
Pumpkin leaf caterpillar
Biology:
- Adult: Moth is medium with whitish wings, transparent with brown marginal patches.
- Larva: Elongate bright green caterpillar is seen with two narrow longitudinal white stripes dorsally.
Life cycle:
Symptoms of damage:
It folds the leaves and scrapes the green matter. As a result the leaves get dried up. It can also feed on ovaries of flower, sometimes bore into young developing fruits.
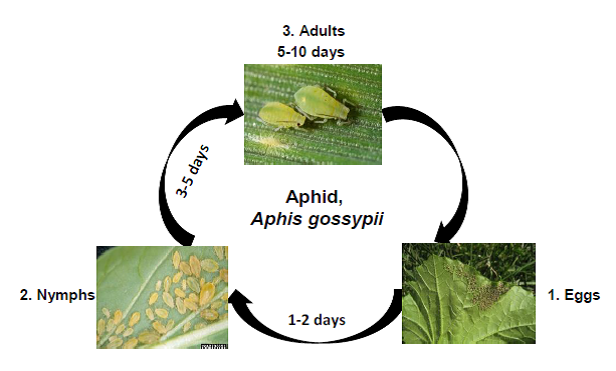
Aphids
This is a cosmopolitan pest and highly polyphagous. It prefers to feed on cotton, cucurbits, eggplant, and okra. Aphids occur during the cool dry season.
Biology:
- Adult: Unlike many insects, most aphids do not lay eggs. They usually reproduce through parthenogenesis (development of embryo without mating with males) and are viviparous (give birth to nymphs directly rather than eggs). The adult color is highly variable and it varies from light green to greenish brown. Both wingless and winged forms occur. Winged forms are produced predominantly under high population density conditions, inferior host plant quality, etc. The wingless forms are more common. They possess a pair of black-colored cornicles on the dorsal side of the abdomen. Aphids mostly are found in groups. Each female produces about 20 nymphs a day, which become adults in a week.
Life cycle:
Parasitoids:

Predators:

IPM for Cucurbitaceous Vegetable
To know the IPM practices for Cucurbitaceous Vegetable, click here
Source: NIPHM, Directorate of Plant Protection, Quarantine & Storage
Last Modified : 3/23/2020
This topic covers information about Amla Insect Pe...
This topic covers information about Insect, Mite A...
This topic covers information about Chilli insect...
This topic covers information about Description of...
