Yogic Management of Obesity
Yogic Management of Obesity
 Obesity is one of the most common nutritional or the metabolic disorder. Obesity is a condition in which excess body fat accumulates to such an extent that health may be negatively affected. Obesity is commonly defined by body mass index (BMI). BMI of 30 kg/m² or higher is considered as obese. This distinguishes it from being overweight as defined by a BMI of 25 kg/m² or higher. Body mass index is a measurment criteria which compares weight & height of the person to categorise him/her as over weight, pre obese or obese.
Obesity is one of the most common nutritional or the metabolic disorder. Obesity is a condition in which excess body fat accumulates to such an extent that health may be negatively affected. Obesity is commonly defined by body mass index (BMI). BMI of 30 kg/m² or higher is considered as obese. This distinguishes it from being overweight as defined by a BMI of 25 kg/m² or higher. Body mass index is a measurment criteria which compares weight & height of the person to categorise him/her as over weight, pre obese or obese.
BMI = Weight (in kg) ÷ Height (in Metre)2
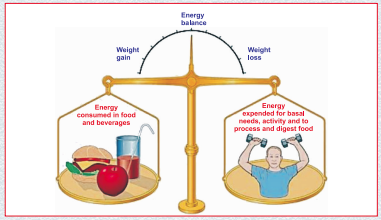
Obesity, in absolute terms, is an increase of body adipose tissue (fat tissue) mass. Obesity is considered as chronic (long-term) disease, like high blood pressure or diabetes. The foods we eat every day contribute to our well- being. Foods provide us with the nutrients we need for healthy bodies and the calories we need for energy. If we eat too much, however, the extra food turns to fat and is stored in our bodies. If we overeat regularly, we gain weight, and if we continue to gain weight, we may become obese.
The excessive fat accumulation can be measured through the following means:
- Skin fold measurements
- Various body circumferences, particularly the ratio of the waist to hip circumference
Causes
A combination of excessive calorie consumption and a sedentary lifestyle are the primary causes of obesity. In a minority of cases, increased food consumption can be attributed to genetic, medical or psychiatric illness. Excess fat accumulation may be due to imbalance between the energy intake and energy expenditure. There are no specific causes as such but factors influencing are :
- Diet : Consumption of High calorie and low-fibre diet.
- Sedentary lifestyle : A sedentary lifestyle plays a significant role in obesity.
- Medical and Psychiatric illness : Certain physical and mental illnesses and the pharmaceutical substances used to treat them can increase the risk of obesity.
- Socio-economic : People of high socio-economic group are more prone to obesity.
- Hereditary : The obesity may inherit from parents to child.
- Endocrine factors : Due to certain hormonal imbalance conditions like in Hypothyroidism, Cushing Syndrome etc.
- Metabolism : The persons whose rate of metabolism is low are at higher risk of becoming obese.
- Psychological factors : Worry, anxiety, fear, feeling of loneliness, dissociation and frustration may stimulate the person to overeat.
- Water retention : Too much consumption of tea, coffee, aerated drinks, soda, soft drinks alcoholic drinks result in deposition of fluid in the body tissues and causes increase in weight.
Complications
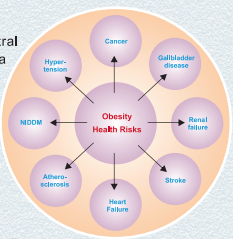 Obesity particularly the central obesity, increases the risk for a number of conditions :
Obesity particularly the central obesity, increases the risk for a number of conditions :
- Diabetes Millitus
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Coronary artery disease : Due to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques in the coronary artery.
- Cerebro-vascular stroke : Not directly linked with obesity but with hypertension Muscles).
- Cholelithiasis (Gall Bladder Stone) : Six times more prevalent in obese subjects than in lean subjects.
- Osteo-arthritis : It is marked adiposity which predisposes to the development of degenerative joint disease.
- Cancers (endometrial, breast and colon)
- Dyslipidemia (High total cholesterol or high levels of triglycerides)
- Sleep apnea
- Gynecological problems (abnormal menses, infertility)
Yogic Management of Obesity
- Om chanting and Prayer
- Shodhana Kriyas : Kapalabhati, Kunjal, Agnisara, Nauli
- Suryanamaskar
- Sukshma Vyayama : Selected practices of Sukshma Vyayama: Udara-sakti-vikasaka (2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 9) (Developing the Abdominal Muscles).
- Yogasanas : Tadasana, Katichakrasana, Urdhwa Hastottanasana, Pawanamuktasana, Sarvangasana, Matsyasana, Halasana, Bhujangasana, Dhanurasana, Uttan Padasana, Paschimottanasana, Ardha Matsyendrasana, Ushtrasana, Mandukasana, Shavasana.
- Pranayama : Nadishodhana, Suryabhedi Pranayama, Bhramari, Sitali, Bhastrika.
- Special Practice : Yoga Nidra
- Dhyana (Meditation) : Om Chanting, Om Meditation
- Yama and Niyama : This will help to have a controlled behavior and would help to pacify the wandering mind and in turn help to have control over the eating and other habits of a person.
Yogic & Diet
Dietary Management
Dietary Management The Yogic diet, popularly known as Satvic diet is the most preferred diet in obese condition. Satvic diet contains more of fresh fruits and vegetables in its natural form, soup etc. Rajasik foods like fried food items, spicy foods, soft drinks and beverages, fast foods etc. should be limited. Tamasik foods like non-vegetarian food items; alcoholic drinks etc. must be avoided.
Prevention of Obesity
- Have regular meals at fixed interval.
- Do not read or watch television while eating.
- Try to keep healthy snacks at home like fruits, vegetables and sprouts instead of cakes, biscuits, fried snacks and other fast foods.
- Do not keep nibbling between meals; eat slowly and chew the food properly.
- Avoid drinking of alcohol and smoking.
- Encourage breast feeding as the child who gets proper breast feeding is less likely to develop obesity in the later age.
- Have control over Carbohydrate intake.
- Physical activity.
Healthwise (For Children)
At Home :
- Don't skip meals; Eat at fixed intervals.
- Don't snack throughout the day.
- Munch fruit whenever feel hungry.
- Limit time on watching television or playing video games, its better to play some outdoor games.
- Play any sport for at least 10 minutes without stopping.
At School :
- Carry home-cooked food in a lunch box and finish it all.
- Avoid junk food from the school canteen and vendors outside.
- Don't bunk the physical education class; play vigorously.
- Don't overeat or skip meals during exams.
When eating out :
- Opt for a salad as a starter.
- Choose water, low fat milk, lassi, tender coconut water etc. instead of a soda
- Opt for steamed, baked, grilled or roasted dishes rather than fried food.
- Order small meals instead of large combos.
Yogic Practices for the Management of Obesity

Last Modified : 8/30/2024
This topic provides information about Desktop Yoga...
This topic covers the information related to cause...
This topic provides information about Yoga for Epi...
This topic deals with information related to Agein...
