Swine Influenza (Swine Flu)
Swine Influenza (Swine Flu)
What is swine flu?
Swine Influenza (swine flu) is a respiratory disease of pigs caused by type a influenza viruses that causes regular outbreaks in pigs. People do not normally get swine flu, but human infections can and do happen. Swine flu viruses have been reported to spread from person-to-person, but in the past, this transmission was limited and not sustained beyond three people.
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of swine flu in people are similar to the symptoms of regular human flu and include fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, headache, chills and fatigue. Some people have reported diarrhea and vomiting associated with swine flu. In the past, severe illness (pneumonia and respiratory failure) and deaths have been reported with swine flu infection in people. Like seasonal flu, swine flu may cause a worsening of underlying chronic medical conditions.
Flu viruses are spread mainly from person to person through coughing or sneezing of people with influenza. Sometimes people may become infected by touching something with flu viruses on it and then touching their mouth or nose.
Infection
Infected people may be able to infect others beginning 1 day before symptoms develop and up to 7 or more days after becoming sick. That means that you may be able to pass on the flu to someone else before you know you are sick, as well as while you are sick.
High risk groups
- Aged 6 months to 4 years;
- Aged 65 years and older;
- Pregnant women;
- Have chronic pulmonary (including asthma), cardiovascular (except hypertension), renal, hepatic, neurologic, hematologic, or metabolic disorders (including diabetes mellitus);
- Immunosuppressed (including immunosuppression caused by medications or by HIV);
- Aged 6 months--18 years and receiving long-term aspirin therapy and who therefore might be at risk for experiencing Reye syndrome after influenza virus infection;
- Residents of nursing homes and other chronic-care facilities;
- Morbidly obese (body-mass index is greater than 40);
- Household contacts and caregivers of persons with serious medical conditions that put them at higher risk for severe complications from influenza;
- Health-care personnel.
Best way to keep away from spreading
If you are sick, limit your contact with other people as much as possible. Do not go to work or school if ill. Cover your mouth and nose with a tissue when coughing or sneezing. It may prevent those around you from getting sick. Put your used tissue in the waste basket. Cover your cough or sneeze if you do not have a tissue. Then, clean your hands, and do so every time you cough or sneeze.
How to protect from Infection
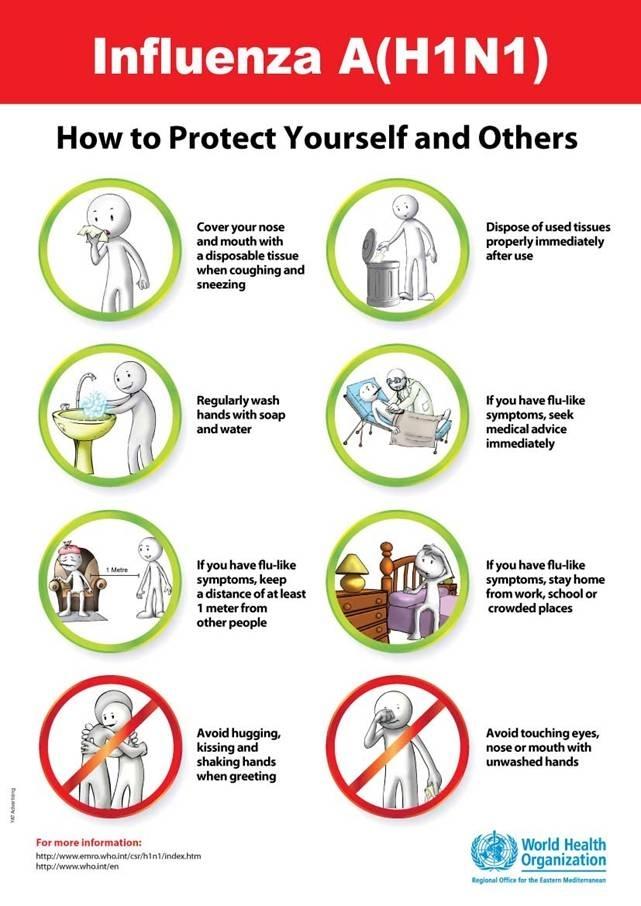
Emergency medical care
In children emergency warning signs that need urgent medical attention include:
- Fast breathing or trouble breathing
- Bluish skin color
- Not drinking enough fluids
- Not waking up or not interacting
- Being so irritable that the child does not want to be held
- Flu-like symptoms improve but then return with fever and worse cough
- Fever with a rash
In adults, emergency warning signs that need urgent medical attention include:
- Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath
- Pain or pressure in the chest or abdomen
- Sudden dizziness
- Confusion
- Severe or persistent vomiting
Do’s and Dont’s
Do’s
- Cover your mouth and nose with a handkerchief or tissue while coughing or sneezing
- Wash your hands every time after coughing or sneezing, thoroughly with soap and water, before and after touching your nose, eyes or mouth
- Avoid crowded places
- Stay at home if infected with flu like illness
- Keep at least an arm’s distance from people affected with symptoms of influenza like cough, running nose, sneezing and fever
- Sleep well, stay physically active and effectively manage stress
- Drink plenty of water and eat nutritious food
Dont’s
- Shake hands, hug and kiss socially, or use other contact greetings
- Take medicines without consulting the physician
- Spit outdoors.
- Aspirin not to be used in children.
H1N1 Virus
The H1N1 virus has created a panic among people across the world, however, the deadly flu has very common symptoms to that of a normal influenza and can be prevented from by following some simple steps.
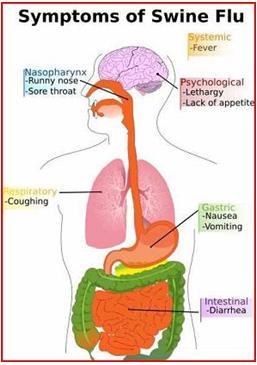
Common Symptoms
- Fever, moderately high, but unlike seasonal flu, can be absent in some cases too
- Nonproductive Cough
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Sore throat
- Body ache
- Headache
- Chills
- Fatigue/tiredness that can be extreme
- Nausea/diarrhoea
- Signs of a more serious swine flu infection might include pneumonia and respiratory failure
Precautions
The deadly Swine Flu has reached the Indian shores following the global outbreak and now, claimed many lives. However, Swine Flu is certainly one of those diseased where an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. Here are five tips for you to keep away from the pandemic.
- If you think you have the H1N1 virus, stay at home and avoid traveling to public places like school and offices; seek medical care IMMEDIATELY.
- Wash your hands frequently: Use the antibacterial soaps to cleanse your hands. Wash them often, for at least 15 seconds and rinse with running water.
- Get enough sleep: Try to get 8 hours of good sleep every night to keep your immune system in top flu-fighting shape.
- Drink sufficient water: Drink 8 to10 glasses of water each day to flush toxins from your system and maintain good moisture and mucous production in your sinuses.
- Always try to cover your nose and mouth with a tissue while coughing or sneezing to avoid passing on infection of any kind to others around you.
- Avoid touching your eyes, nose and mouth to prevent the spread of the virus.
- Try and maintain contact with ill persons or someone who is showing symptoms of the flu.
- Boost your immune system: Keeping your body strong, nourished, and ready to fight infection is important in flu prevention. So stick with whole grains, colorful vegetables, and vitamin-rich fruits.
- Keep informed: The government is taking necessary steps to prevent the pandemic and periodically release guidelines to keep the pandemic away. Please make sure to keep up to date on the information and act in a calm manner.
Related resources
- Frequently Asked Questions – influenza a (H1N1) (216KB)
- Government Authorized Hospitals for Treatment of Swine Flu (96.8KB)
- Hand Wash (457KB)
- Toll Free helpline Numbers for Swine Flu Information (141KB)
- Technical guidelines
- Ayurveda Prospective of Swine Flu
- Seasonal influenza (H1N1)- WHO
- List of outlets having schedule X license authorized to sell oseltamivir formulation for SWINE FLU
Last Modified : 2/12/2020
This topic explains about psychological human deve...
This topic provides information about Zero tillage...
This topic provides information related to steps t...
This topic provides about *99# Service- Innovative...

