Jeevika Model: Community Engagement in Ending TB
Jeevika Model: Community Engagement in Ending TB
Introduction and Rationale
India, with an estimated 2.6 million Persons with TB (PwTB), has the highest burden of TB in the world. The country accounts for 26% of the global TB burden, 27% of drug-resistant TB (DRTB) cases, 36% of TB deaths, and the largest number of TB-HIV co-infected PwTB. Although there has been an increase in TB notification over the years, thereby reducing the missing cases, but the gap remains. There is a need to focus more on vulnerable people through TB elimination efforts.
Poor living conditions of migrants give rise to sub-standard environmental conditions coupled with high population density, making them more vulnerable to lung diseases, including asthma and TB. The proper understanding of health-seeking behaviour among the vulnerable could reduce delay in diagnosis, improve treatment compliance and improve health promotion strategies, particularly for TB.
The National Strategic Plan (NSP) of the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP) for 2017-25 emphasizes the need for the community’s active participation in ending TB. KHPT is implementing ‘Breaking the Barriers’ project in Bihar funded by USAID for migrants and the urban vulnerable population.
Objectives
To develop and implement community engagement strategies for vulnerable population groups such as the urban vulnerable and migrants for increased case detection, notification and successful treatment outcomes.
Overall approach and Key Strategies
The following activities have been undertaken:
- Consultation / key informant interviews and interactions with persons working for TB control in the district
- Validating information through focus area mapping
- Shortlist formal, informal and traditional community networks ( Jeevika Groups) that exist within each of the vulnerable groups using a checklist and conduct consultation with shortlisted groups
- Conduct perspective-building workshops with the key leaders from these selected Jeevika Groups on health and TB, the community’s role, PwTB needs and vulnerabilities, and linkages, and develop a local action plan
- Regular handholding meetings with Jeevika (cluster meeting, Voluntary Organization meeting & SHG Meetings)
Implementation
The project’s duration is for four years (March 2020 - March 2024). The table below provides information on the geographies, vulnerable population, and coverage as part of the initiative.
| State | Districts | Type of Vulnerable Population | No.of TUs | No.of Focus Area Mapping sites covered |
Total Population in the TUs | Total Vulnerable Population in the TUs |
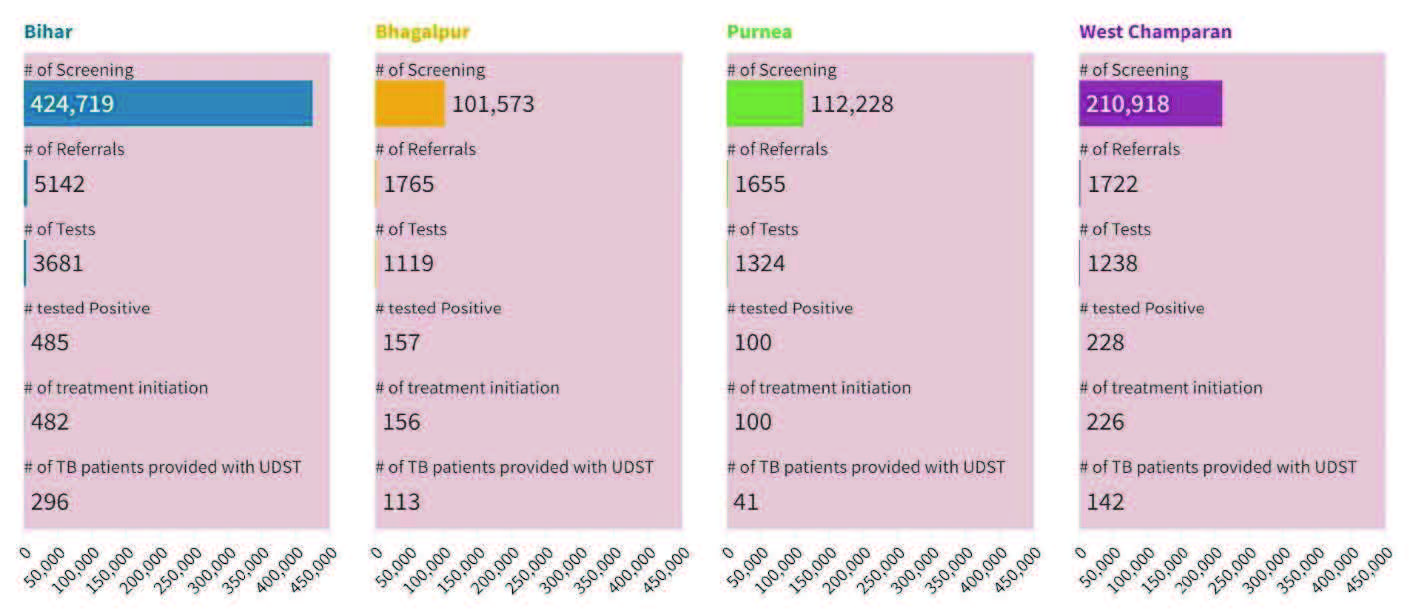
| Bihar | Bhagalpur | Urban Vulerable Population | 8 | 45 | 462974 | 86297 |
| Purnea | Migrants | 8 | 329 | 2248052 | 154170 | |
| West Champran | Migrants | 8 | 249 | 2837797 | 318136 | |
| Migrants & Urban Vulnerable | 24 | 623 | 5548823 | 558603 |
Outcomes
Mapping of Vulnerable Population :
| S.No | Indicator | Bhagalpur | Purnea | West Champaran | Bihar |
| 1 | No of Jeevika Groups Shortlisted | 239 | 614 | 537 | 1390 |
| 2 | No of Jeevika Groups Shortlisted | 189 | 490 | 537 | 1216 |
| 3 | No of Perspective Building Workshops conducted | 22 | 40 | 34 | 96 |
| 4 | No of Jeevika Groups participated in PBW | 172 | 415 | 450 | 1037 |
| 5 | No of Jeevika members trained | 539 | 983 | 855 | 2377 |
Awareness for General Population:
| S.No | Indicator | Bhagalpur | Purnea | West Champaran | Bihar |
| 1 | No of Awareness programs conducted by Jeevika groups | 1004 | 1393 | 1618 | 4015 |
| 2 | No of Health Camps conducted by Jeevika Groups | 28 | 44 | 17 | 89 |
| 3 | No of Jeevika groups which support persons with TB with non-medical needs | 95 | 248 | 104 | 447 |
Key Recommendations:
To effectively use the community structures, it is necessary to follow below steps-
- Training of Health staff/Trainers at state/district level
- Identification of villages/sites with a significant vulnerable population
- Listing and training of selected Community Structures/Jeevika Groups working for vulnerable population
- Handholding of CS during weekly/monthly meetings
- Supporting CS in awareness generation, screening and referral
- Data analysis and gap identification
- Documentation of community engagement effort
Potential for replication and scale-up
Community structures like Jeevika reach each and every individual in the community. They are working to generate awareness in the vulnerable community and refer presumptive persons. They are also supporting the treatment adherence of persons with TB, and offer linkages to non-medical support, e.g. nutrition support.
The pilot shows that there is enormous potential with these community structures. Jeevika is a formal structure with saving and lending as their primary function, but this intervention has showed that the Jeevika leaders have the potential to think and act beyond their assigned tasks and are ready to take up health agenda for the community.
Source : TBC India
Last Modified : 4/30/2024
This topic provides information about Pan Masala B...
This topic provides information about MOBILE KUNJI...
Provides information about contact details of dist...
This topic provides information about KILKARI : Mo...
