Exercise for good health
Exercise for good health
Be physically active and exercise regularly to maintain good health
Rationale: Regular physical activity, yoga and exercise keep one physically and mentally fit and promote good health.
- Regular physical activity, yoga and exercise of moderate intensity are recommended for good health and wellbeing
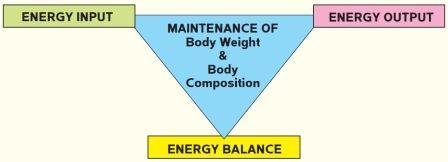
- These help in maintaining desirable body weight, muscle strength, bone health, flexibility of joints and appropriate body mass composition, which are of vital significance for health.
- Regular physical activity, yoga and exercise reduce the risk of non-communicable chronic diseases. Being physically active can reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, osteoporosis, arthritis and certain types of cancer.
- Lack of physical exercise impairs health but over exertion could be detrimental.
- A minimum 30–45 minutes brisk walk / physical activity of moderate intensity among adults helps in maintaining good health.
- Regular physical activity of 60 minutes per day among children can prevent overweight / obesity.
- Even among people with chronic diseases, physical activity helps in maintaining health.
- It creates a sense of wellbeing, increases confidence and avoids depression.
- Yoga is a holistic, structured and planned physical activity that also includes breathing exercises as well as physical and mental relaxation (meditation).
What is physical activity?
Physical activity can be classified as structured or incidental:
- Structured activity is planned and repetitive in nature and includes exercises such as aerobics, stretching and strengthening activities (brisk walk, gym workouts, swimming, jogging, skipping, cycling, etc.).
- Yoga is a holistic, structured and planned physical activity that also includes breathing exercises (pranayama) as well as physical and mental relaxation (meditation).
- Incidental activities include a broad range of routine activities such as household chores, walking around for daily tasks, climbing up the stairs, gardening, leisure activities, work place activities, leisure games and sports.
Types of physical activity and health benefits
A combination of physical activities is recommended for overall health and improved cardio-respiratory and muscular fitness. It can be broadly classified into four types: endurance, strength, balance and flexibility.
- Aerobic /Endurance activities : This activity tends to increase the heart rate and breathing, resulting in greater improvement in the heart and lung functioning. Most often it is called cardio activity or endurance activity. The activities range from brisk walking (moderate) to running or jogging or swimming or bicycling (vigorous).
- Muscle and bone strengthening activities : These activities come under resistance training or weightlifting or weight loading or weight bearing. These activities include lifting heavy objects/ weights, carrying a child, working with elastic bands, pushups, crunches, squats, jumping rope, etc. Weight-bearing exercises can improve muscle and bone strength.
- Balance activities : These activities improve flexibility, agility, gait and include exercises such as lunges, walking backward, dancing, stretching and martial arts, etc.
- Flexibility / Yoga : Includes all the above three categories of activities along with flexibility and breathing exercises as well as physical and mental relaxation exercises.
Based on their intensity and the level of physical activity, activities can be classified into the following categories:
- Sedentary activity : Those who are engaged in activities with postures of sitting, standing up and walking around in the home, workplace or community. These activities cause a slight increase in breathing rate than when being at rest. Light activities include walking at <3km per hour on level ground, cleaning the house, cooking, etc.
- Moderate activity : Those involved in activities requiring some effort, like walking at a brisk pace of 3–6 km/hour on a level firm ground, aerobic activities, gardening, hiking, yogasanas and pranayama, gentle swimming, playing outdoor/indoor games such as badminton, tennis, table tennis, etc. It is described by a noticeable increase in depth and frequency of breathing, while continuing to be able to talk.
- Vigours (Heavvy aсtivity): Those engaged in activities requiring significant effort, like aerobics, running, jogging at >7 km/hour, jumping rope, participating in some competitive sports, quarrying, mining, etc. These activities are described by a greater increase in depth and rate of breathing, making it harder to breathe and not allowing the individual to talk freely
Guidelines for physical activity
- If one follows sedentary life style, it is wise to consult a doctor before starting an exercise program.
- Exercise intensity and duration should be increased gradually over a period of time. Shortness of breath, pain, nausea, vomiting, and headache are warning signs that your body needs rest.
- Children and adolescents (>5–19 years): It is recommended to do a minimum of 60 minutes per day of moderate-to- vigorous intensity activity. Vigorous intensity activities and strength training should be included for at least three days per week.
- Adults (>19–60 years): It is recommended to do a minimum of 30–60 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity per day for at least five days in a week; or 15 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity per day for at least five days in a week depending on age and health condition; or an equivalent combination of moderate and vigorous-intensity activity. Muscle strengthening exercises, activating all muscle groups should be performed for a minimum of two days in a week.
- Elderly (>60 years): The recommendations for this group are similar to that of adults. They are required to include additional activities that enhance strength and functional balance for three days or more in a week.
Recommended Physical Activity: Duration for good health
- Sleep : 480 min.
- Occupation (work) : 480 min.
- Household chores (cleaning, cooking or washing utensils) : 220 min.
- Personal care / eating / watching TV : 180 min.
- Leisure time physical activity (different yoga postures, walking, gardening, dancing etc.) : 60 min.
- Aerobic exercise (brisk walking, running, Swimming, cycling etc.) : 20 min.
Some tips to keep physically active even when on a busy schedule
- At work, use a standing desk or stand every half hour.
- Walk for 5–10 minutes every few hours.
- Take all phone calls walking, both at work place or home.
- Use stairs instead of lifts/elevator.
- Park vehicle away from work place.
- While watching TV, move around every few minutes or during commercial breaks.
- As you get up in the morning, do some simple yoga and stretches to keep your muscles active and joints flexible.
- Regular strength training with weights is necessary to maintain muscle mass and improve metabolism. Not using muscles causes muscle atrophy.
- Perform two to three weight-bearing exercise per week to delay age-related muscle loss.
- Certain yoga postures (asanas) combined with breathing exercises are known to speed up the metabolism and help burn fat and facilitate weight loss.
General tips for physical activity
- Reduce the time involved in sedentary activities and increasing time spent in moderate-to-vigorous intensity activities.
- Increase the time in movement at work place or at home.
- Parents and schools should encourage children to involve in 60 minutes of moderate-to-vigorous intensity of activities every day.
- Adults and older population should involve in around 20–40 minutes per day of moderate-intensity and 10–20 minutes per day of vigorous-intensity activities.
- People with illnesses or chronic diseases like heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, asthma, osteoporosis and obesity should consult a physician before taking up an exercise program.
- Men and women over 40 years of age should also consult a doctor or healthcare provider before starting a vigorous physical activity program.
Source: ICMR National Institute of Nutrition, Hyderabad - Dietary guidelines for Indians
Last Modified : 5/14/2024
This topic covers the Information related to Breas...
This topi covers the information related to Hygeni...
This topic covers the information related to advan...
This topic provides information for students on id...
