Safety for Health Care Providers
Safety for Health Care Providers
- Health Care Worker Safety
- Eliminating needle recapping
- First Aid management of the Exposure to Blood and Body Fluid Exposure during Injection Procedure
- Preventing Reuse of Injection Equipment
- Reasons for the injection giver to purposefully reuse injection equipment
- Preventing Re-Use
- Security of injection devices
Health Care Worker Safety

- Rational use of injections: Substitute injections by administering, medications through another mute such as tablet, inhaler etc. where ever possible. As mentioned, about 70% of the injections could be avoided through judicious mix of clinical decisions.
- Immunization against HBV: This should be insured for every health care worker. Every health care institute’s human resource department could facilitate adherence to this, even for contractual workers and staff engaged in any type of health care plan.
- Implementing Universal Precautions: Bio safety measures for medical waste disposal should be strictly followed at the point of waste generation. Use of Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) by healthcare worker should be encouraged, following the NACO guidelines. The PEP protocols should be prominently displayed and rotational nodal officers should be designated on round the clock basis.
Eliminating needle recapping
- Disposing of the sharp into a sharps container immediately after use
- Use of safer devices such as needles i.e. safety needles and cannulas
- Provision and use of personal protective equipment, and
- Training of workers regarding the risks and prevention of transmission of infections.
First Aid management of the Exposure to Blood and Body Fluid Exposure during Injection Procedure
| Injury or Exposure | Management |
|
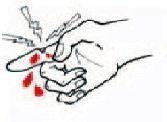
Needle-stick or other sharps injury
|
Imrnediately wash the affected area with soap and water Allow injury to bleed freely and report immediately to higher authority. Report to the higher authority where PEP is available DO NOT suck blood fiom the site NOT squeeze out blood |
|
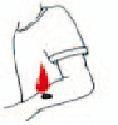
Splash of blood and/or body fluids on non-intact skin
|
Splash of blood and/or body fluids on non-intact skin NOT use disinfectant on skin NOT scrub or rub the area. NOT squeeze or press the area |
|
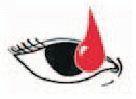
Splash of blood or body fluids to eyes
|
Flush the area gently but thoroughly with running water or saline for at least 15 minutes while the eyes are open Keep eyelid gently inverted |
|
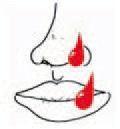
Splash of blood or body fluids to mouth
|
Immediately spit out the blood or fluids and rinse the mouth with water several times
|
|
Splsh of blood or body fluids on intact Skin
|
Immediately wash the affected area with soap and water DO NOT rub the area |
Preventing Reuse of Injection Equipment
A challenge Reuse of syringes and needles simply means using the same needle and/or syringe more than one time for injection preparation or administration. These could be reused either intentionally in the hospital at the point of care (Intentional Re-use) or picked up at the point of disposal for repackaging and recirculation in the market (Downstream reuse). Reuse of syringes and improper waste disposal needlessly expose patients, health care workers and community to deadly blood-borne pathogens, such as HBV, HCV and HIV.
Reasons for the injection giver to purposefully reuse injection equipment
- Lack of awareness
- Altruism - limited number of syringes; many patients in need
- Economic reasons - reuse for financial gain.
Preventing Re-Use
- In order to address this issue, a three pronged strategy is needed
- Proper training to health care staff including bio medical waste management workers
- Carrot and Stick measures backed by appropriate policy and guidelines
- Use of technology in terms of re- use prevention feature enabled injection devices. WHO has recommended use of Auto Disable syringes in Immunization since 2002 across the globe. As only 5-10% injections are given for Immunization and rest for therapeutic reasons, there are Re Use Prevention (RUP) and Prefilled syringes available to make injections safer and adhere to WHO best practice of “prevent access to used syringes and needles".
Security of injection devices
- Appropriate financing procurement and supply managements to be ensured in a timely manner.
- Ensure adequate supply of injectable products including diluents wherever applicable, appropriate single use injectable device & functional hub cutters/sharps containers/safety boxes for waste disposal.
- Reliable distribution system for health products so as to ensure availability of all supplies in timely manner and in adequate quantity
Last Modified : 2/21/2020