National Strategy for Financial Education 2020-2025
National Strategy for Financial Education 2020-2025
Strengthening Financial Inclusion in the country has been one of the important developmental agendas of both the Government of India and the four Financial Sector Regulators (viz. Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI), Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) and Pension Fund Regulatory Authority of India (PFRDA). Financial literacy supports the pursuit of financial inclusion by empowering the customers to make informed choices leading to their financial well-being.< p/>
Subsequent to completion of the period of the first National Strategy for Financial Education (NSFE: 2013-2018), a review of the progress made was undertaken by the Technical Group on Financial Inclusion and Financial Literacy (TGFIFL- Chair: Deputy Governor, RBI) under the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC-Chair: Hon’ble Union Finance Minister). Based on the review of progress made under the Strategy and keeping in view the various developments that have taken place over the last 5 years, notably the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), the National Centre for Financial Education (NCFE) in consultation with the four Financial Sector Regulators and other relevant stakeholders has prepared the revised NSFE (2020-2025).
The NSFE document intends to support the Vision of the Government of India and Financial Sector Regulators by empowering various sections of the population to develop adequate knowledge, skills, attitude and behaviour which are needed to manage their money better and plan for their future. The Strategy recommends adoption of a Multi-Stakeholder Approach to achieve financial well-being of all Indians.
Financial literacy and Education
Financial Literacy is defined as a combination of financial awareness, knowledge, skills, attitude and behaviour necessary to make sound financial decisions and ultimately achieve individual financial well-being (OECD, 2012).
Financial Education, on the other hand is defined as the process by which financial consumers/investors improve their understanding of financial products, concepts and risks and through information, instruction and/or objective advice, develop the skills and confidence to become more aware of financial risks and opportunities, to make informed choices, to know where to go for help and to take other effective actions to improve their financial well-being” (OECD, 2005)
Strategic objectives
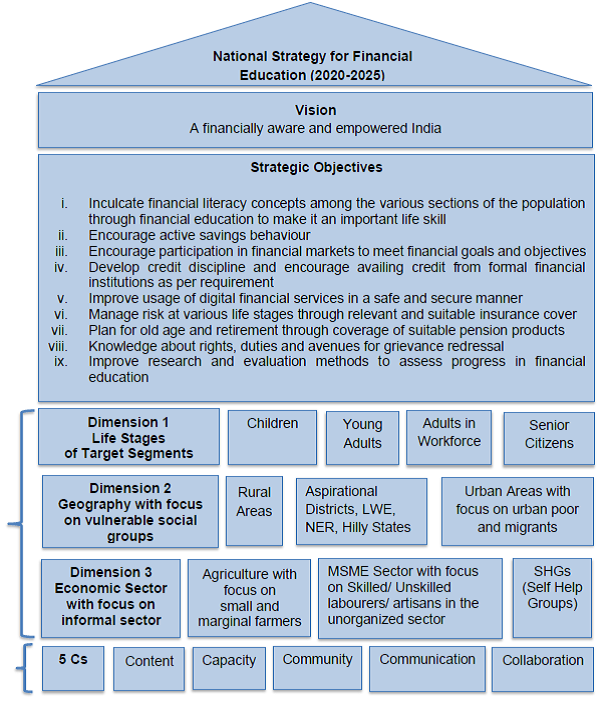
To achieve the vision of creating a financially aware and empowered India, the following Strategic Objectives have been laid down:
- Inculcate financial literacy concepts among the various sections of the population through financial education to make it an important life skill
- Encourage active savings behaviour
- Encourage participation in financial markets to meet financial goals and objectives
- Develop credit discipline and encourage availing credit from formal financial institutions as per requirement
- Improve usage of digital financial services in a safe and secure manner
- Manage risk at various life stages through relevant and suitable insurance cover
- Plan for old age and retirement through coverage of suitable pension products
- Knowledge about rights, duties and avenues for grievance redressal
- Improve research and evaluation methods to assess progress in financial education
Approach
In order to achieve the Strategic Objectives laid down, the document recommends adoption of a ‘5 C’ approach for dissemination of financial education through emphasis on development of relevant Content (including Curriculum in schools, colleges and training establishments), developing Capacity among the intermediaries involved in providing financial services, leveraging on the positive effect of Community led model for financial literacy through appropriate Communication Strategy, and lastly, enhancing Collaboration among various stakeholders.
The recommendations laid down in the Strategy under each of the ‘5 Cs’ are as under:
Capacity
- Develop the capacity of various intermediaries who can be involved in providing financial literacy.
- Develop a ‘Code of Conduct’ for financial education providers.
Community
- Evolve community led approaches for disseminating financial literacy in a sustainable manner.
Communication
- Use technology, mass media channels and innovative ways of communication for dissemination of financial education messages.
- Identify a specific period in the year to disseminate financial literacy messages on a large/ focused scale.
- Leverage on Public Places with greater visibility (e.g. Bus Stands, Railway Stations, etc.) for meaningful dissemination of financial literacy messages.
Collaboration
- Preparation of an Information Dashboard.
- Integrate financial education content in school curriculum, various Professional and Vocational courses (undertaken by Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSD&E) through their Sector Skilling Missions and the likes of B.Ed./M.Ed. programmes.
- Integrate financial education dissemination as part of various on-going programmes.
- Streamline efforts of other stakeholders for financial literacy.
The Strategy also suggests adoption of a robust ‘Monitoring and Evaluation Framework’ to assess the progress made under the Strategy.
Overview of NSFE (2020-2025)
Source : National Strategy for Financial Education 2020-2025
Last Modified : 7/13/2021
This topic provides information about Livelihood G...
This topic provides information about Sewa Mitra P...
This topic provides information about Raj-Kaushal:...
This topic provides information about Employment G...
