Local Economic Development
Local Economic Development
- Introduction
- Why Panchayats?
- How do we begin to plan for local economic development in the Gram Panchayat?
- What can our Gram Panchayat focus on while planning for local economic development?
- How do we set targets to achieve the goals?
- What can a Gram Panchayat Do?
- Resources to look for
- People to support
- Here is an example:
- How is this exercise linked to Sustainable Development Goals?
- The Universal Targets
Introduction
Local economic development is not just about development of basic needs of individuals but about people working together to achieve sustainable economic growth and improved lives. Employment and income are needed to prosper.This implies creation of more employment in the Gram Panchayats, promotion of entrepreneurship and addition of further opportunities for economic growth.
For local economic development potential from natural resources may be assessed by:
- Listing the potential of production and diversity from agricultural land,water bodies, forest, animal husbandry.
- Listing the inputs required for enhanced productivity such as irrigation,modern cultivation technologies like precision farming, polyhouses,integrated nutrient, pest and water management, cold storage and godowns.
These inputs can result in enhanced farm income and generation of employment.To institutionalize this growth farmer producer organizations (FPO) and labour banks.may be promoted.
‘Amul’ is the world’s largest FPO. It made India the largest producer of milk in the world. ‘Amul’ is also the world’s leader in milk processing technology and marketing. It originated from the villages. Why are we not able to replicate it in other sectors and areas?
Several other measures may be considered for local economic development:
- Facilities such as reliable power, water, measures for safe processing of solid and liquid wastes, vector free environment can be identified and small industrial parks can be set up.
- Quality control laboratories may be facilitated in association with schools and PHCs and common package facilities can be created alongwith a brand in the Gram Panchayat’s name. These facilities can be used as incubation centres if linked with polytechnics, engineering colleges or food technology institutes.
- Local consumption demands may be met through local enterprises and by leveraging local cooperative banks.
- Mechanization of agriculture may be initiated and labour banks be created for local employment provision.
Building of self help group of poor men and women in neighbourhood may be a good starting point for all these activities. This will create an enabling environment for thrift and credit, micro finance, opening of bank accounts, linkages with banks etc. Thus financing a micro enterprise will become easier within a short span of time.
Why Panchayats?
The activities mentioned above conform to the subjects of the Panchayats as per the 11th Schedule of the 73rd amendment of the Constitution of India -Small scale industries, including food processing industries, Khadi, village and cottage industries, Technical training and vocational education, Minor forest produce, Fisheries, Animal husbandry, dairying and poultry, Agriculture, including agricultural extension. Above all, one of the objectives laid out in the 73rd amendment to the constitution is local economic development!
For local economic development Gram Panchayats can work to:
| MAP |
Micro, small and medium enterprises within the panchayat area |
|
| Enterprise opportunities in the village | ||
| Employment opportunities for different categories and degrees of disabilities | ||
| IDENTIFY AND TRACK | Potential candidates to set up enterprises. | |
| Skills of interested candidates . | ||
| FACILITATE | Prevention of child labour and create awareness on prevention of child labour | |
| Jobs under MGNREGS. | ||
| Availability of facilities at MGNREGS worksite. | ||
| Prevention of manual scavenging | ||
| Rehabilitation of and cash assistance for manual scavengers through the social welfare department | ||
| Entrepreneurial development training | ||
| Handholding support for new enterprises | ||
| Job creation through convergence of ongoing schemes and sponsorships. | ||
| MAINTAIN | Database on labour and employment | |
| Categorization of disabled based on nature and degree of disability. | ||
| CREATE | Awareness on equal wages for men and women for equal work | |
| IEC material on labour legislations, rights and entitlements. | ||
| Village-level child protection committees and promote child protection services. | ||
How do we begin to plan for local economic development in the Gram Panchayat?
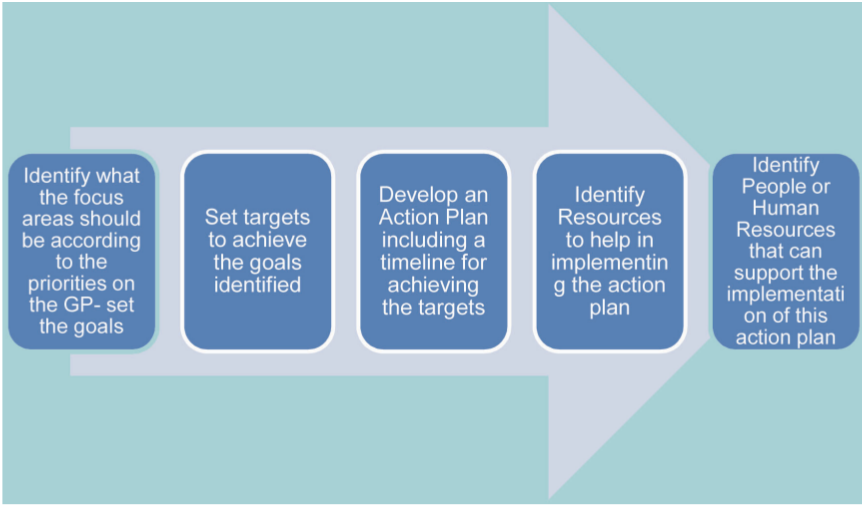
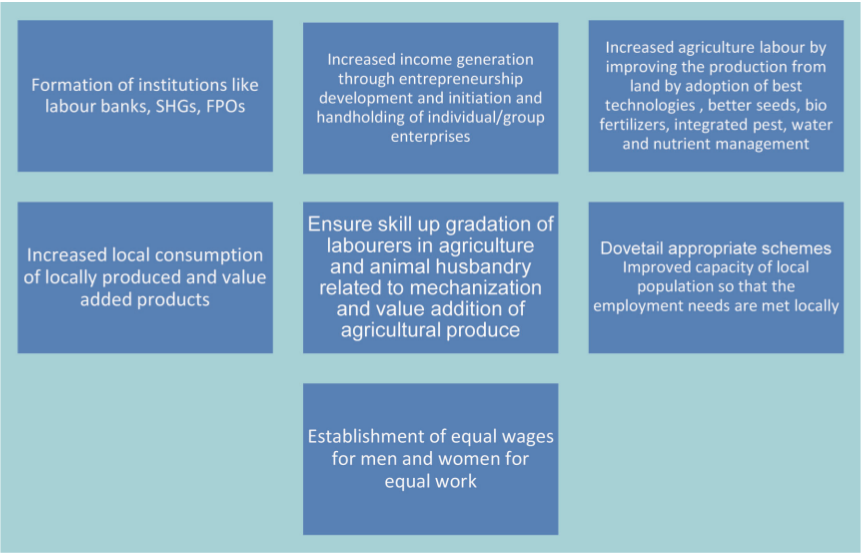
What can our Gram Panchayat focus on while planning for local economic development?
- Maximized production and employment opportunities through agriculture, animal husbandry, pisciculture, and by adoption of best technologies and practices.
- Value added products from agriculture, animal husbandry, pisciculture,non-timber forest produce.
- Assured employment opportunities for all households in the village.
- Ensuring the income of labourers to a level on par with other jobs and vocations in the country.
- Ensuring equitable wages for men and women, zero child labour.
- Employment opportunities for persons with disabilities.
How do we set targets to achieve the goals?
If these are our goals, what are the specific things we should plan to achieve and by when? Can our Gram Panchayat plan for the following?
What can a Gram Panchayat Do?
- Identify all people in the productive age who have no/under employment and map their skills.
- Map and list various production potential/labour potential/enterprise opportunities in the village.
- Map employment opportunities suitable to persons with disabilities based on nature and degree of disability and facilitate job creation through convergence of ongoing schemes, sponsorships and ensuring local placements.
- Identify potential candidates for setting up of enterprises and skill mapping of the interested candidates.
- Situation analysis of existing micro, small and medium enterprises within the Panchayat area.
- Organize entrepreneurial development training/skill training.
- Create effective and sustained mechanisms for liasoning and converging resources from various government departments, statutory agencies,financial agencies, R&D institutes, and educational institutions.
- Provide handholding support for new enterprises/institutions.
Resources to look for
| Deen Dayal Antyodaya Yojana (DAY)-National Rural Livelihoods Mission (NRLM) and other government schemes for enterprise development |
| Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) |
| Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDU-GKY) |
| The Prohibition of Employment as Manual Scavengers and their Rehabilitation Act, 2013 |
| State-sponsored schemes, other department schemes, youth welfare schemes |
People to support
SHGs, local professionals, social workers, successful Swarnajayanti Gram Swarojgar Yojana (SGSY) entrepreneurs, successful local entrepreneurs,Anganwadi workers, literacy activists, teachers, NRLM CRPs, MGNREGS mates,youth organizations, Rural Development Department, Department of Social Justice.
Here is an example:
How can a Gram panchayat plan for local economic development
Let us go through a case study from a state;
PSC Bank Limited is a small cooperative bank catering to the needs of about 5000 households in a Panchayat. The bank routinely lends money to farmers for the cultivation of paddy, coconut, banana, vegetables, animal husbandry,poultry etc. It also has programmes for drip irrigation, irrigation wells, cattle sheds, bio gas tanks .
The bank also facilitates a mechanized labour bank involved in agriculture operations such as all paddy operations, coconut harvesting, vegetable cultivation and animal husbandry.
But maintaining the momentum became a tough task because of the fluctuations of the market. Initially a place was set up for the farmers to sell their items during specific hours and days. This was later converted in to a modern super market where farmers need not be present to sell. Whatever they brought in- even in small quantities - the supermarket purchased it and displayed it aesthetically for sale. The gap in local produce was filled from externally brought produce to ensure the customer did not experience difficulty. Local credit cards were issued to the member farmers so that their consumption is fully met. The very fact that materials were produced locally attracted external buyers also.
Now the supermarket is selling produce worth Rs 5 lakhs per day, one fourth locally produced materials and all 5000 families have a regular and stable income. New value addition facilities are steadily coming up! Their social security is also taken care of by the Bank.
How is this exercise linked to Sustainable Development Goals?
Sustainable Development Goal 8 - Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all.
The Universal Targets
- Promote development oriented policies that support productive activities,decent job creation, entrepreneurship, creativity and innovation, and encourage the formalization and growth of micro, small- and medium-sized enterprises, including through access to financial services.
- By 2030 achieve full and productive employment and decent work for all women and men, including for young people and persons with disabilities,and equal pay for work of equal value.
- By 2020, substantially reduce the proportion of youth not in employment,education or training.
- Take immediate and effective measures to eradicate forced labour, end modern slavery and human trafficking and secure the prohibition and elimination of the worst forms of child labour, and by 2025 end child labour in all its forms.
Now look at the goals and targets set by your Gram Panchayat – you are contributing to the Global goal and targets to promote sustainable economic growth, productive employment and decent work for all!
Source : Handbook on Sustainable Development Goals and Gram Panchayats
Last Modified : 6/19/2024
This topic provides information about 20th Livesto...
The Article provides information about Antioxidant...
This topic deals with information related to Appen...
This topic provides information about Sim Card Swa...
