Bracon Pupal cards
Bracon Pupal cards
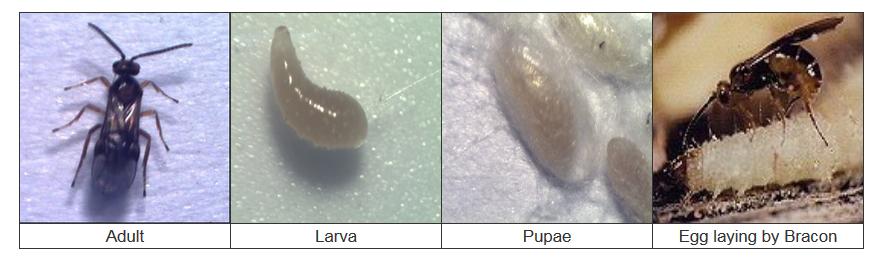
Bracon hebetor Say and B. brevicornis (Wesmael) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) are highly polyphagous, gregarious, and ecto-larval parasitoids of several species of Lepidopteran larvae. They parasitize a variety of important Lepidopteran pests of stored product and field crops (Dabhi et al. 2011). Among the common insect pests that are hosts of Bracon are rice moth (Corcyra cephalonica), angoumois grain moth (Sitotroga cerealella), wax moth (Galleria mellonella), Indian meal moth (Plodia interpunctella), castor shoot and capsule borer (Conogethes punctiferalis), castor semilooper (Achaea janata), cabbage head borer (Hellula undalis), gram pod borer (Helicoverpa armigera), spotted pod borer (Maruca testulalis), spotted bollworm (Earias vittella), tobacco caterpillar (Spodoptera litura), cabbage leaf webber (Crocidolomia binotalis), sorghum/maize stem borer (Chilo partellus), pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella) and coconut black headed caterpillar (Opisina arenosella) (Dabhi et al. 2011, Anonymous 2013).
Bracon spp. are important parasitoids of O. arenosella and parasitism was observed throughout the year, it ranged from 26.2 to 26.7% during the peak period of infestation. It attacks the larval stage of the insect host and lays eggs on the surface of the host insect. Larvae upon hatching start feeding on host body fluids by inserting their mouth parts into host. From each host larvae 2 or more parasitoid larvae develop and pupate.
Release Rates
4000-5000 pupae cocoons ha-1 or 2000-5000 adults ha-1 will effectively control the pests. Depending upon the need weekly releases need to be made.
Release Methods
- Stapling Bracon card with pupae
- Releasing adults collected from sandwich or tub method
- Releasing adults in tub method
Mass Production
Sandwich method

Tub method

Last Modified : 5/18/2024
This topic covers information about Mass productio...
This article covers the occurrence and biological ...
This topic provides information about Preparation ...
