Yogic Management of Bronchial Asthma
Yogic Management of Bronchial Asthma
Introduction
The asthmatic disorder is a chronic (recurring) inflammatory condition in which the airways develop increased responsiveness to various. stimuli, characterized repeated episodes of wheezing, breathlessness, chest tightness and cough that is at least partly reversible, either spontaneously or with treatment. It is thought that inflammation causes an increase in airway responsiveness (broncho- spasm) to a variety of stimuli. Some of these stimuli would have little or no effect on non-asthmatics with normal airways. Many cells play a role in the inflammatory response.
Asthma causes narrowing of airways and broncho-spasm. Airway narrowing process basically involves :
- Tightening of the smooth muscles around the airways,
- Swelling of the airways, and
- Collecting of thick mucus secretions in the airways
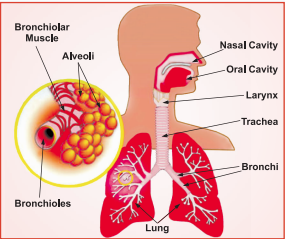 This narrowing of airways causes symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing, which respond to bronchodilators (medicines).
This narrowing of airways causes symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing, which respond to bronchodilators (medicines).
People with asthma have extra sensitive or hyper-responsive airways. The airways react by narrowing when they become irritated (by asthma triggers). This makes it difficult for the air to move in and out of the lungs.
Asthma often occurs in episodes called asthma attacks. An asthma attack is usually caused by triggers or changes in the environment. Common triggers include infections, changes in the weather, exercise, allergens and irritants in the environment.
Asthma has such a wide spectrum of predisposing factors and clinical presentations that there is no uniform classification. Based on the severity of symptoms, it is categorized into mild intermittent, moderate and severe.
Other clinical categories include steroid-dependent, steroid- resistant, difficult, and brittle asthma. Typically, asthma is categorized into
- Extrinsic : initiated by a type I hypersensitivity reaction induced by exposure to an extrinsic antigen
- Intrinsic : initiated by diverse, non-immune mechanism including ingestion of aspirin; pulmonary infections especially viral, cold, inhaled irritants, stress and exercise.
Other informal categories classify asthma according to the agents or events that trigger broncho-constriction. These include seasonal, exercise-induced, drug-induced, and occupational asthma and asthmatic bronchitis in smokers. Allergic broncho-pulmonary aspergillosis, which may complicate asthma, is partly an allergic reaction to fungus that has called colonized the bronchial mucosa.
Signs and Symptoms of Asthma
- Asthma is characterized by difficulty in breathing, wheezing and cough.
- Difficulty in expiration.
- Tightness of the chest/ discomfort in the chest.
- Attacks last from one to several hours.
- Severe attacks may affect the heart and circulatory system.
- Severe attack, not responsive to usual therapy is called "status asthmaticus" and is a medical emergency.
- Hypercarbia (increased level of CO₂), acidosis and hypoxia (decreased O₂ level) is rare in Asthma.
Patho-physiology of Bronchial Asthma
↓
Edema of bronchial mucosa
↓
Increased bronchial secretions
↓
Gases trapped in alveoli & reduced ventilation
↓
Coughing, shortness of breathing & wheezing
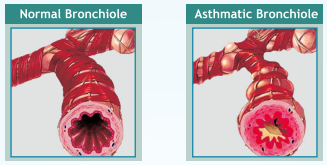 Inhalation of allergen rapidly interact with mucosal mast cells results in increase of histamine and cysteinyl leukotrienes which leads to broncho-constriction. Airflow is restricted by narrowing of airways. This narrowing occurs due to irritation of the bronchial walls, which leads to swelling of the lining of the bronchi and to the secretion of mucus. During respiratory distress asthmatics use the accessory muscles of respiration. This panicking act makes breathing even more difficult.
Inhalation of allergen rapidly interact with mucosal mast cells results in increase of histamine and cysteinyl leukotrienes which leads to broncho-constriction. Airflow is restricted by narrowing of airways. This narrowing occurs due to irritation of the bronchial walls, which leads to swelling of the lining of the bronchi and to the secretion of mucus. During respiratory distress asthmatics use the accessory muscles of respiration. This panicking act makes breathing even more difficult.
During an asthma episode, inflammed airways react to environmental triggers such as smoke, dust or pollen. The airways narrow and produce excess mucus, making it difficult to breathe.
The airways of asthma patients are hypersensitive to certain triggers. In response to exposure to these triggers, the bronchi (large airways) contract into spasm (asthma attack). Inflammation soon follows, leading to a further narrowing of the airways and excessive mucus production, which leads to coughing and other breathing difficulties.
Bronchial asthma triggers
Bronchial asthma triggers may include :
- Tobacco smoke
- Infections such as colds, flu or pneumonia
- Allergens such as food, pollen, mold, dust mites and pet dander
- Exercise
- Air pollution and toxins
- Weather, especially extreme changes in temperature
- Drugs (such as aspirin, NSAID and beta-blockers)
- Food additives (such as MSG)
- Emotional stress and anxiety
- Smoking, perfumes, or sprays
- Acid reflux
- Occupational irritants (gases, fumes, vapors, dust, tobacco or other smoke, air pollution of any kind)
- Microscopic droppings of dust mites and cockroaches, airborne pollens and molds, plants and plant proteins, enzymes, and pet dander (minute scales of hair, feathers or skin)
- Viral, sinus infections such as a cold
- Exposure to an allergen (for which the person is allergic)
Management of Bronchial Asthma
Dietary Management
- The diet plays an important role in the management of asthma.
- There are foods, which are allergic to asthma patient and such foods should be avoided. These foods include cold foods, ice creams, chocolates, other stimulants, fruits like banana, milk & milk products etc.
- Foods which add to the mucous production should be specifically avoided.
- Try to take warm water/ drinks
- Avoid ghee, butter, oily, spicy and other Kapha aggravating diet.
- When you have asthma attack, avoid taking food after sunset.
Yogic Management
The role of Yoga in the management of Bronchial asthma is well documented now. Aim of the treatment in Asthma should be to prevent the broncho-constriction and to tackle the triggering factors.
- Shatkriyas : Jalaneti, Sutraneti, Kapalabhati, Kunjal, Vastra dhouti
- Om chanting and Prayer
- Suryanamaskara
- Selected practices of Sukshma Vyayama : Uccarana sthala tatha Visuddha chakra shuddi, Buddhi tatha dhriti shakti vikasaka, Vaksha sthala shakti vikasaka - 1 and 2
- Yogasanas : Tadāsana, Katichakrasana, Urdhwa hastottanasana, Gomukhasana, Ushtrasana, Vakrasana, Bhujangasana, Sarvangasana, Sarala Matsyasana, Shavasana
- Pranayama : Full yogic breathing, Nadishodhana Pranayama, Suryanadi Pranayama, Bhramari, Bhastrika
- Special Practice : Yoga Nidra/ Antarmouna
- Dhyana (Meditation) Om Chanting, Om Meditation
Yogic Practices for the Management of Bronchial Asthma

Last Modified : 8/30/2024
This topic provides information about Homoeopathy ...
This topic gives complete Information related to D...
This topic provides information about Yogic Manage...
Provides information about Do’s and Don’ts of Yoga...
