National Health Accounts Estimates for India
National Health Accounts Estimates for India
About National Health Accounts Estimates for India
The National Health Account (NHA) estimates for India is an annual publication that provides estimates of healthcare expenditures in India. The NHA estimates are prepared by using an accounting framework National Health Accounts Guidelines for India, 2016 (with refinements where required) that adheres to the System of Health Accounts 2011 (SHA 2011), a global standard framework for producing health accounts developed by the World Health Organization (WHO).
The report is published by The National Health Systems Resource Centre (NHSRC), designated as the National Health Accounts Technical Secretariat (NHATS) in August 2014 by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare with a mandate to institutionalize Health Accounts in India.
The report is being published since 2013-14.
What are Health Accounts?
Health Accounts describe health expenditures and flow of funds in the country’s health system over a financial year of India. It answers important policy questions such as what the sources of healthcare expenditures are, who manages these, who provides health care services, and which services are utilized. It is a practice to describe the health expenditure estimates according to a global standard framework, System of Health Accounts 2011 (SHA 2011), to facilitate comparison of estimates across countries. SHA 2011 framework presents expenditures disaggregated as Current and Capital expenditures. Focus is on describing Current Health Expenditures (CHE) and their details presented according to
- Revenues of healthcare financing schemes - entities that provide resources to spend for health goods and services in the health system;
- Healthcare financing schemes - entities receiving and managing funds from financing sources to pay for or to purchase health goods and services;
- Healthcare providers - entities receiving finances to produce/ provide health goods and services;
- Healthcare Functions - describe the use of funds across various health care services
National Health Account estimates for India 2020-21 and 2021-22
The NHA estimates for 2021-22 show that Government expenditure for healthcare continues to increase in the country, highlighting the efforts of the Government to increase public investments in the health sector. The share of Government Health Expenditure (GHE) in the overall GDP of the country has increased from 1.13% in 2014-15 to 1.84% in 2021-22. In terms of share in the General Government Expenditure (GGE), it has increased from 3.94% in 2014-15 to 6.12% in 2021-22.
In per capita terms, GHE has tripled, from Rs. 1,108 to Rs. 3,169 between 2014-15 to 2021-22. The Government spending on health between 2019-20 and 2020-21 increased by 16.6%, while between 2020-21 and 2021-22, it grew by an unprecedented rate of 37%, highlighting the proactive role played by the Government in tackling the COVID-19 pandemic.
The increase in Government spending on health has an important implication for the reduction of financial hardship endured by households. In the Total Health Expenditure (THE) of the country between 2014-15 and 2021-22, the share of GHE has increased from 29% to 48%. During the same period, the share of Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OOPE) in THE declined from 62.6% to 39.4%.
The continuous decline in the OOPE in the overall health spending vindicates the substantial efforts made by the Government in the progress towards ensuring financial protection and Universal Health Coverage for its citizens.
Another positive trend in the country’s health financing space is the increase in Social Security Expenditure (SSE) on healthcare. This increase in social security has a direct impact on reducing out-of-pocket payments. A robust social security mechanism ensures that individuals will not face financial hardship and the risk of poverty as a consequence of accessing essential healthcare services. The share of SSE on health, which includes Government-funded health insurance, medical reimbursement to Government employees, and social health insurance programs, in THE, has increased from 5.7% in 2014-15 to 8.7% in 2021-22.
The NHA Estimates for 2020-21 and 2021-22.
National Health Account (NHA) estimates for India 2019-20
National Health Account (NHA) estimates for India 2019-20 is the seventh consecutive NHA estimates report prepared by NHSRC, designated as National Health Accounts Technical Secretariat (NHATS) in 2014 by the Union Health Ministry. With the present estimate of NHA, India now has a continuous series of NHA estimates for the country, from 2013-14 to 2019-20. These estimates are not only comparable internationally, but also enable the policymakers to monitor the progress in different health financing indicators of the country.
Highlights of NHA Estimates 2019-20
- For the year 2019-20, Total Health Expenditure (THE) for India is estimated to be Rs. 6,55,822 crores (3.27% of GDP and Rs. 4,863 per capita).
- Current Health Expenditure (CHE) is Rs. 5,93,659 crores (90.52% of THE) and capital expenditures is Rs. 62,163 crores (9.48% of THE). Capital expenditures are reported for all sources of Government (Union Government is Rs. 22,923 crores; State Government Rs. 38,951 crores; external donors Rs. 289 crores).
- Government Health Expenditure (GHE) including capital expenditure is Rs. 2,71,544 crores (41.41% of THE, 1.35% GDP, and Rs. 2,014 per capita). This amounts to about 5.02% of General Government Expenditure in 2019-20. Of the GHE, Union Government’s share is 35.8% and State Governments’ share is 64.2%.
- Household’s Out of Pocket Expenditure on health (OOPE) is Rs. 3,40,916 crores (47.07% of THE, 1.54% of GDP, Rs. 2,289 per capita) Private Health Insurance expenditure is Rs. 45,838 crores (6.99% of THE).
- Distribution of Current Health Expenditure (2019-20) according to Healthcare Financing Schemes, Revenues of Healthcare Financing Schemes, Healthcare Providers and Healthcare Functions (%)
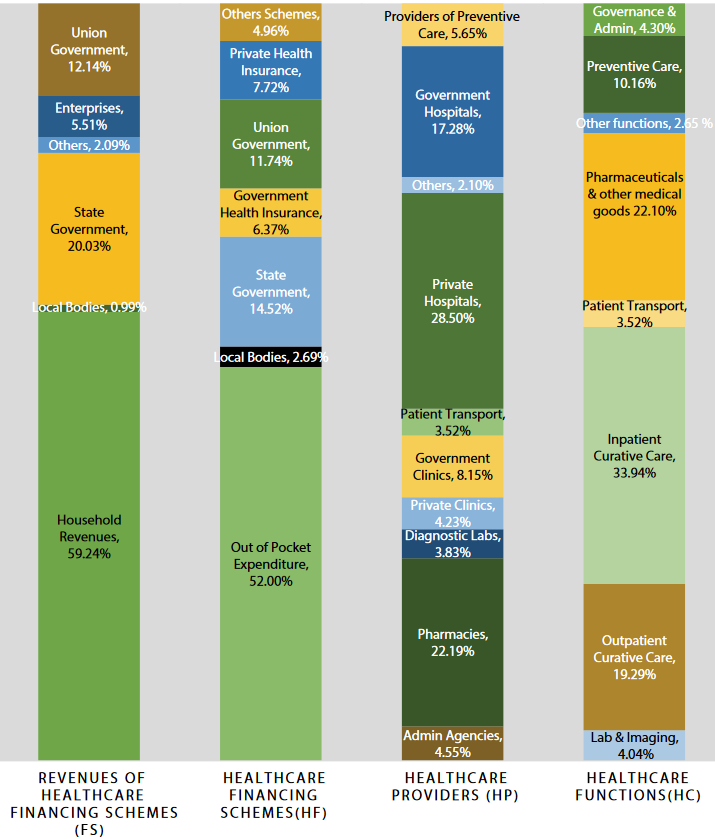 Key observations
Key observations
- The share of Out-of-Pocket Expenditure (OOPE) in total Health Expenditure (THE) declined from 62.6% to 47.1%. The continuous decline in the OOPE in the overall health spending show progress towards ensuring financial protection and Universal Health Coverage for citizens.
- The share of Government Health Expenditure (GHE) in the overall GDP of the country has increased from 1.13% in 2014-15 to 1.35% in 2019-20.
- In per capita terms, GHE has doubled from Rs. 1,108 to Rs. 2,014 between 2014-15 to 2019-20. The government spending on health between 2018-19 and 2019-20 increased by 12%, more than double the growth rate between 2017-18 and 2018-19 which was at 5%.
- Additionally, in General Government Expenditure (GGE), the share of health sector spending has steadily increased from 3.94% to 5.02% between 2014-15 and 2019-20.
- In the Total Health Expenditure (THE) of the country between 2014-15 and 2019-20, the share of GHE has increased from 29% to 41.4%.
- Social Security Expenditure (SSE) on healthcare - The share of SSE on health, which includes government-funded health insurance, medical reimbursement to government employees, and social health insurance programs, in THE, has increased from 5.7% in 2014-15 to 9.3% in 2019-20.
To read the complete report, click here.
Previous National Health Accounts estimates
To read the previous NHA estimates for the country, from 2013-14 to 2019-20, click here.
Source : NHSRC
Last Modified : 9/25/2024
Reserve Bank of India releases the statistical pub...
This topic provides information related to Nationa...
